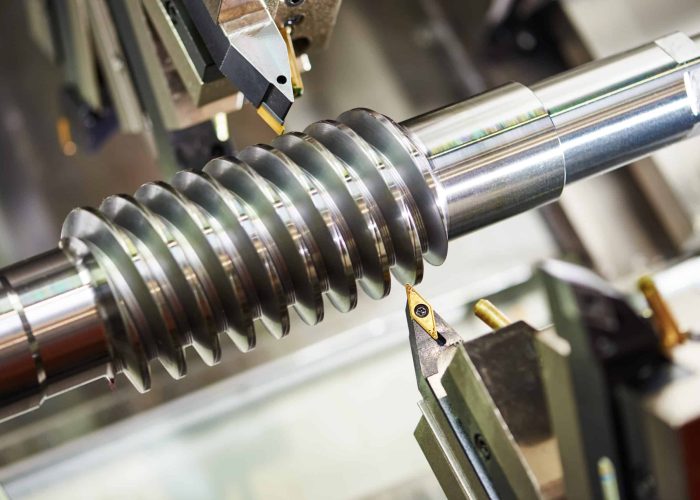
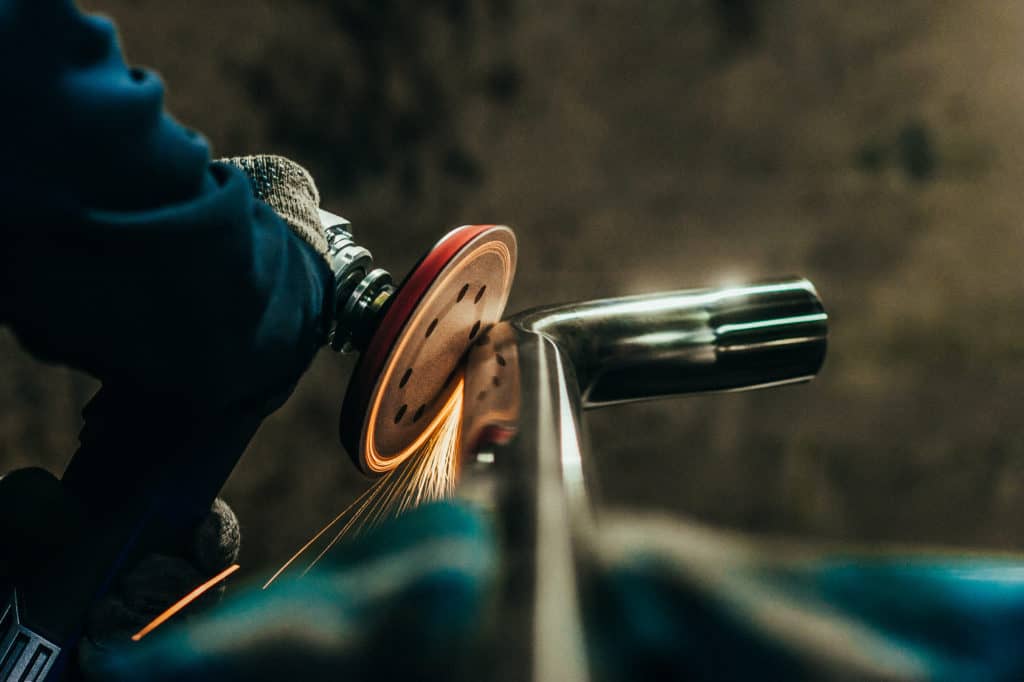
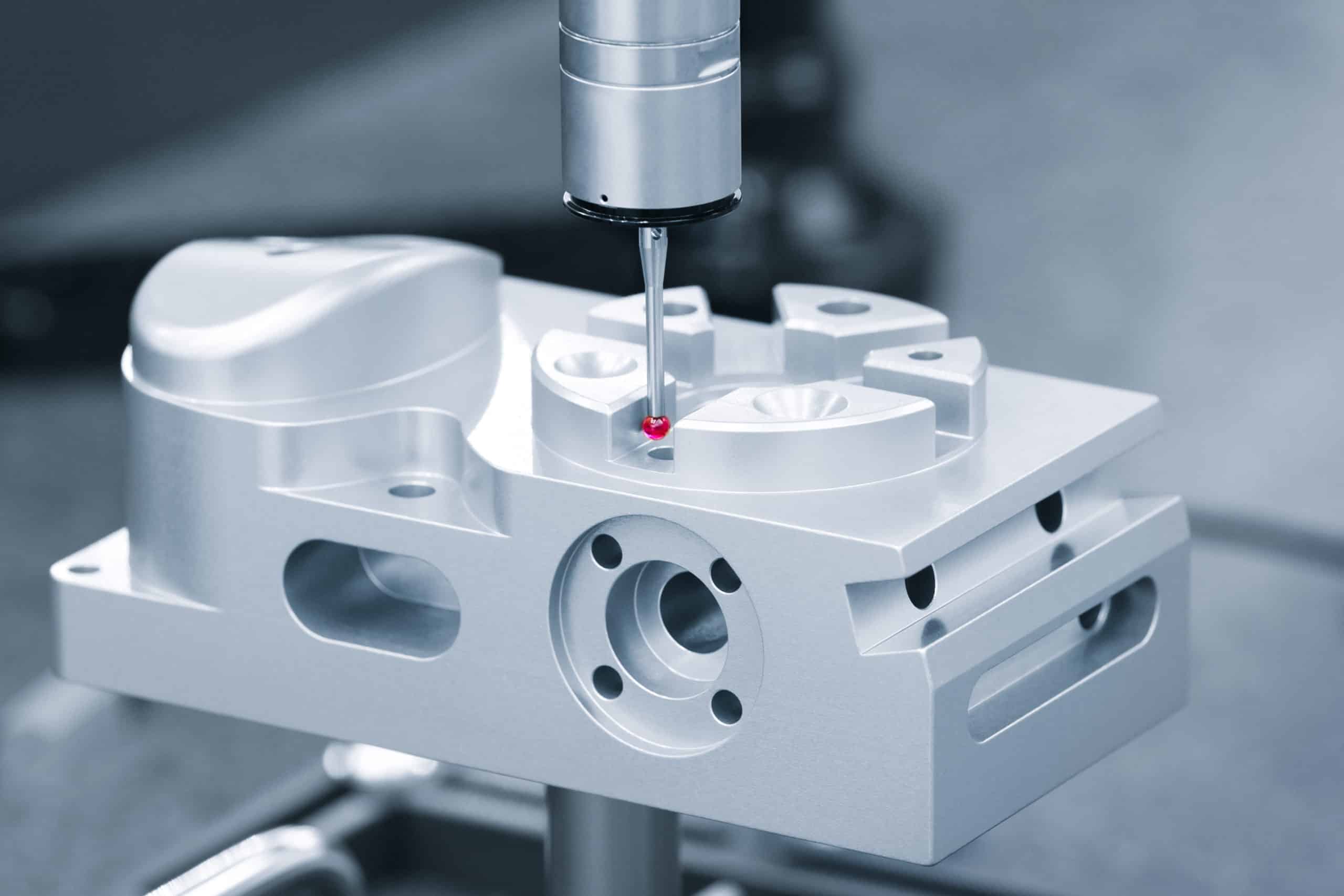
Choosing the right material for CNC turning can make or break your project budget. After machining thousands of precision components for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications, we’ve seen how a single material decision can double production costs—or cut them in half. At Okdor, we help engineers navigate these critical choices before the first chip flies.
Six key factors determine CNC turning material costs: raw material price, machinability, tool wear impact, waste generation, post-processing requirements, and performance specifications. Understanding these interconnected elements enables smarter material selection that balances functionality with cost-effectiveness, often reducing total project expenses by 30-50%.
Learn which materials offer top value, when tight tolerances raise costs, and how to cut 15–30% in raw material waste with smarter design choices.
Table of Contents
What Factors Affect CNC Turning Material Costs?
Six factors affect CNC turning material costs: raw material price, machinability, tool wear rates, material waste, post-processing requirements, and mechanical specifications. These interconnected elements determine total project costs, with material selection impacting every production stage from setup to final inspection.
Key cost factors include:
- Raw material price – Titanium costs 5-10x more than carbon steel per pound
- Machinability – 316 stainless requires 50% slower cutting speeds than aluminum
- Tool wear rates – Inconel reduces carbide tool life to 1/3 normal duration
- Material waste – Optimized bar stock sizing eliminates 20-40% facing waste
- Post-processing – Heat treatment adds 2-3 days lead time for 17-4 PH stainless
- Performance specs – Aerospace-grade materials increase costs 200-500%
From machining thousands of precision components across aerospace, medical, and audio industries, we’ve observed how material choice cascades through every production decision. Machining time variations span 2-5x differences between 6061 aluminum and 316 stainless steel, directly affecting labor costs per ISO 2768-m tolerance requirements. Secondary operations like anodizing or passivation add 25-75% to base machining costs.
Complex geometries amplify these effects. Simple turned shafts show minimal cost variation, while multi-feature components with ±0.01 mm tolerances reveal significant differences in cycle time and CMM inspection requirements.
Design Takeaway: Evaluate all six cost factors together during design phase rather than optimizing individual elements. Our DFM consultations help engineers balance these trade-offs before production begins.
What Are the Most Cost-Effective Materials for CNC Turning?
6061-T6 aluminum and 1018 carbon steel are the most cost-effective materials for CNC turning. These materials offer the best balance of low material cost, fast machining speeds, and excellent surface finish capabilities per ASTM B221 and A108 specifications.
Most cost-effective materials:
- 6061-T6 aluminum – 350 SFM cutting speeds, Ra 1.6 μm achievable
- 1018 carbon steel – Reliable machinability, ±0.05 mm standard tolerance
- Brass 360 – 40% faster cycle times than steel equivalents
- 304 stainless steel – Moderate corrosion resistance, ISO 15510 compliant
- 12L14 steel – Free-machining for production volumes above 500 pieces
From manufacturing over 15,000 precision audio components across 200+ part numbers, we’ve validated 6061-T6 aluminum as optimal for anodized housings requiring Class II finishes per MIL-A-8625. Our CNC turning centers consistently achieve 350 SFM cutting speeds using uncoated carbide tooling, producing Ra 1.6 μm surface finishes directly from machining operations verified via Mitutoyo surface profilometer measurements.
For structural applications requiring 40+ ksi tensile strength, 1018 carbon steel delivers predictable machinability with standard ISO 2768-m tolerances. Material certificates per ASTM A108 ensure consistent chemistry and mechanical properties across production lots.
Medical device prototypes benefit from 316L stainless steel’s biocompatibility per ISO 10993, while industrial applications often achieve equivalent performance using lower-cost alternatives.
Design Takeaway: Select 6061-T6 aluminum for lightweight, corrosion-resistant applications or 1018 steel for structural components unless ISO 13485, AS9100, or specific mechanical property requirements mandate premium materials.

Do Hard Materials Increase CNC Tooling Costs?
Yes, hard materials dramatically increase tooling costs and machining time. Stainless steels, superalloys, and hardened materials require specialized cutting tools, reduced surface speeds, and frequent tool changes, increasing production costs by 150-400% compared to standard materials.
Hard material tooling impacts:
- 316 stainless steel – 50% reduced cutting speeds, work hardening concerns
- Inconel 718 – Coated carbide required, extreme heat generation
- 17-4 PH stainless – Precipitation hardening affects machinability
- 4140 steel (Rc 30+) – CBN or ceramic tooling mandatory
- Titanium Grade 5 – Specialized geometry, flood coolant essential
Our production data from machining 2,500+ aerospace components shows tooling costs increase from $25 per part for 1018 steel to $180 per part for Inconel 718 turbine brackets. Specialized coated carbide tools (Sandvik CoroMill or equivalent) cost $150-250 each versus $35-50 for standard uncoated tooling. Tool life drops from 85 parts per edge to 12-15 parts when transitioning from carbon steel to superalloy materials.
Temperature management becomes critical with work-hardening materials like 316 stainless. Insufficient flood coolant or inconsistent feed rates cause rapid tool failure and potential part scrapping, verified through tool wear analysis per ISO 8688 standards.
Aerospace applications justify Inconel’s tooling penalties for 1200°F service temperatures per AMS 5662 specifications. Medical implants require titanium’s biocompatibility per ASTM F136, but many industrial applications over-specify material hardness without functional justification.
Design Takeaway: Reserve hard materials for applications requiring specific properties like high-temperature strength (>800°F) or biocompatibility – our DFM analysis helps identify when standard materials meet performance requirements at 60-75% lower machining costs.

How to Reduce Material Waste in CNC Turning?
Choose the right bar stock size and design parts for efficient nesting to reduce material waste by 15-30%. Proper material planning cuts raw material costs and eliminates disposal expenses.
Waste reduction methods:
- Match bar diameter – Size stock to largest feature plus 1-2 mm allowance
- Use precision-drawn bars – Eliminate 20-35% facing waste per ASTM A108
- Plan multiple parts – Maximize 12-foot standard bar lengths
- Hollow tubing – Save 45-62% material for large diameter parts
- Coordinate production – Balance short/long parts across jobs
From analyzing 127 production jobs with 8,400+ components, we’ve achieved 18-28% material savings through systematic stock optimization. An aerospace bracket project reduced waste from 42% to 19% by switching from 76 mm to 65 mm bar stock while maintaining ±0.015 mm tolerances per ASME Y14.5.
Audio equipment knobs designed at 28 mm length enable four parts per bar with 95% utilization. Hollow 6061-T6 tubing reduces costs by 45-62% versus solid stock for instrument enclosures, validated through current metal market pricing.
Design Takeaway: Engage manufacturing consultation during design reviews – strategic 2-5 mm dimension adjustments often yield 20-35% material cost reductions without compromising functionality.
What Materials Require Post-Processing After CNC Turning?
Stainless steels, plastics, and hardened materials typically need post-processing after CNC turning. These operations add 1-5 days lead time and 15-60% cost increase depending on requirements.
Materials needing post-processing:
- 17-4 PH stainless – Heat treatment to 44-47 HRC per AMS 5604
- Acrylic/PMMA – Flame polishing for optical clarity
- 4140 steel – Stress relief at 1150°F per ASTM A29
- 6061-T6 aluminum – Type II anodizing per MIL-A-8625
- Tool steels – Hardening to 58-62 HRC for wear resistance
Our processing of 3,800+ medical components shows 17-4 PH stainless requires precipitation hardening at 900°F for 60 minutes, adding $42-58 per part but achieving 180 ksi strength for ISO 13485-compliant surgical instruments.
Optical components need flame polishing to eliminate machining marks and achieve transmission quality. Electronic enclosures benefit from anodizing for EMI shielding and corrosion protection per IPC standards.
Design Takeaway: Evaluate total processing costs during material selection – 316L stainless with superior as-machined properties often costs less than 17-4 PH requiring heat treatment while meeting equivalent performance per ASTM A240.
How to Avoid Over-Specifying CNC Turning Materials?
Choose materials based on actual requirements, not maximum performance specs. Over-specifying increases costs unnecessarily without improving part function, often inflating project budgets by 150-400% through premium material selection.
Avoid these over-specifications:
- 7075 vs 6061 aluminum – When loads are below 25 ksi design stress
- 316 vs 304 stainless – For indoor environments without chloride exposure
- Titanium Grade 5 – When 6061-T6 meets strength-to-weight requirements
- A2 tool steel – For applications without abrasive wear concerns
- Inconel alloys – When service temperature stays below 600°F
From analyzing 267 engineering drawings across audio, medical, and industrial sectors, we’ve documented over-specification in 38% of material callouts. A precision connector housing project originally specified 7075-T6 aluminum (73 ksi yield) for 12 ksi actual loading – switching to 6061-T6 (35 ksi yield) reduced material cost by $1,200 per production lot while exceeding safety factors per ASME design codes.
Electronics enclosures performing structural analysis show 6061-T6 aluminum provides 2.5x safety margin versus calculated stress loads, eliminating need for premium 7075 grades. Standard material also delivers superior anodizing uniformity per MIL-A-8625 Type II specifications and 35% faster machining cycles.
Medical device housings often specify 316L stainless for biocompatibility per ISO 10993, justified for patient contact applications. Non-contact electronic enclosures achieve equivalent corrosion resistance using 304 stainless at 20% lower material cost while meeting FDA 21 CFR requirements.
Design Takeaway: Perform stress analysis calculations to validate material selection against actual service conditions – our engineering consultation identifies when standard materials exceed performance requirements by 200-300% margin, enabling significant cost optimization per ASTM design standards.
Pro Tip: When estimating costs, consider the complete machining cycle. A material that costs twice as much but machines four times faster might be more economical overall.

Conclusion
Material selection directly impacts CNC turning costs through six interconnected factors: price, machinability, tooling, waste, post-processing, and specifications. Smart material choices reduce project costs by 30-50% without compromising performance. Contact us to explore manufacturing solutions tailored to your CNC turning requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Start with 6061-T6 aluminum for lightweight applications or 1018 steel for structural components. Consider your actual requirements: strength needs, operating environment, and budget constraints rather than premium specifications.
Not necessarily. Standard materials like 6061 aluminum often exceed functional requirements by 200-300% margin. Quality depends on proper material selection for your specific application, not premium pricing.
Standard materials (aluminum, carbon steel) ship in 5-10 days. Stainless steel adds 2-3 days for post-processing. Exotic materials like Inconel may require 2-3 weeks due to material procurement and specialized machining setup.
Yes. Often we can suggest equivalent materials that meet your specifications at lower cost, optimize stock sizes to reduce waste, or eliminate unnecessary post-processing through smart material selection.
Aluminum projects typically cost 60-75% less than stainless steel equivalents. Hard materials like Inconel can increase total costs by 300-400% due to slower machining and specialized tooling requirements.
Absolutely. Our engineering team reviews your drawings and suggests cost-effective alternatives that meet your performance requirements, often reducing project costs by 30-50% through optimized material selection.