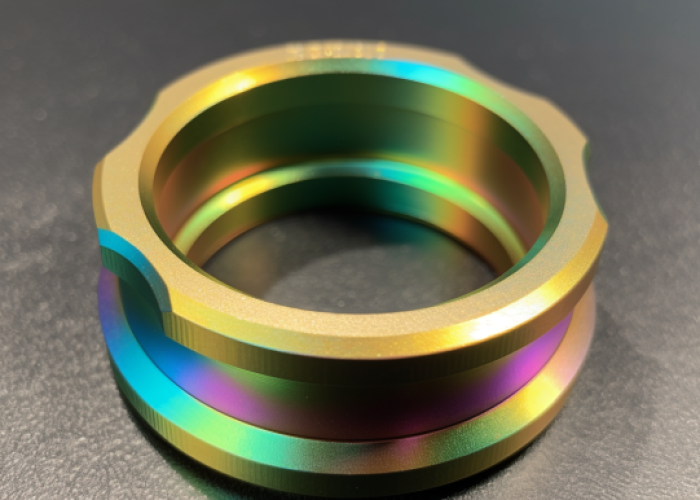
Choosing the right surface finish for CNC aluminum parts affects both cost and performance. At Okdor, we help engineers across aerospace, medical, and audio industries make finish decisions that optimize project outcomes. This guide answers the key questions about alodine coating: when to use it, tolerance effects, and application suitability.
Alodine coating is a chromate conversion coating that creates a 0.5-4 micron protective film on aluminum without affecting CNC part dimensions or tolerances. This chemical process provides corrosion resistance, maintains electrical conductivity, and improves paint adhesion for precision components.
Learn how alodine works, its surface finish impact, cost versus anodizing, and design guidelines for your CNC aluminum projects.
Table of Contents
What Is Alodine Coating for CNC Aluminum Parts?
Alodine coating is a chemical conversion process that transforms aluminum surfaces into a thin, corrosion-resistant chromate film measuring 0.5-4 microns thick. Unlike paint or plating, this process chemically bonds with the aluminum substrate to create protective chromium oxide compounds without affecting part dimensions—essential for maintaining CNC machining tolerances.
Key Alodine Coating Properties:
- Ultra-thin film: 0.5-4 microns (vs 10-25 microns for anodizing)
- Dimensional preservation: No impact on CNC tolerances or threaded features
- Electrical conductivity: Maintains aluminum’s conductive properties
- Chemical bonding: Forms chromium oxide layer through surface conversion
- Self-limiting process: Consistent thickness regardless of part geometry
We routinely apply alodine coating to precision aluminum components across aerospace, medical, and audio applications. The chromate conversion process occurs when parts are immersed in trivalent or hexavalent chromium solutions, creating a controlled reaction that produces the protective film. This chemical reaction forms a golden-yellow to clear protective layer that automatically stops growing once equilibrium is reached.
For CNC machined parts, alodine coating offers distinct advantages over thicker finishes. The ultra-thin film preserves threaded features, press-fit tolerances, and assembly interfaces without requiring design modifications. Unlike anodizing, alodine maintains electrical conductivity while providing an ideal base for subsequent painting or powder coating operations.
Design Takeaway: Specify alodine coating when your CNC aluminum parts require corrosion protection without dimensional changes, particularly for assemblies needing electrical continuity or superior paint adhesion.
What Are the Benefits of Alodine Coating on Aluminum?
Alodine coating provides superior corrosion resistance, maintains electrical conductivity, and improves paint adhesion for precision aluminum components. This combination of protective and functional properties makes it ideal for applications requiring both durability and performance in demanding environments.
Primary Alodine Coating Benefits:
- Corrosion protection: Forms barrier against moisture, chemicals, and environmental exposure
- Electrical conductivity: Retains aluminum’s conductive properties for grounding and electrical applications
- Paint adhesion: Creates chemically bonded surface for superior coating performance
- Process efficiency: Simple chemical treatment without electrical current requirements
- Cost effectiveness: Lower processing costs compared to anodizing or other surface treatments
Alodine-coated aerospace components routinely exceed 500-hour salt spray testing requirements, demonstrating exceptional corrosion resistance in saltwater and high-humidity environments. The coating’s electrical conductivity makes it essential for audio equipment housings and medical device enclosures where grounding is critical for safety and performance.
The paint adhesion properties are particularly valuable for multi-stage finishing processes. Alodine creates a slightly roughened surface with excellent chemical bonding characteristics, reducing paint failure and improving long-term durability compared to coating bare aluminum directly. This prevents common issues like paint chipping and flaking on untreated aluminum surfaces.
Design Takeaway: Choose alodine coating when your application requires corrosion protection plus electrical conductivity or superior paint adhesion, especially for components exposed to harsh environments or requiring subsequent painting.
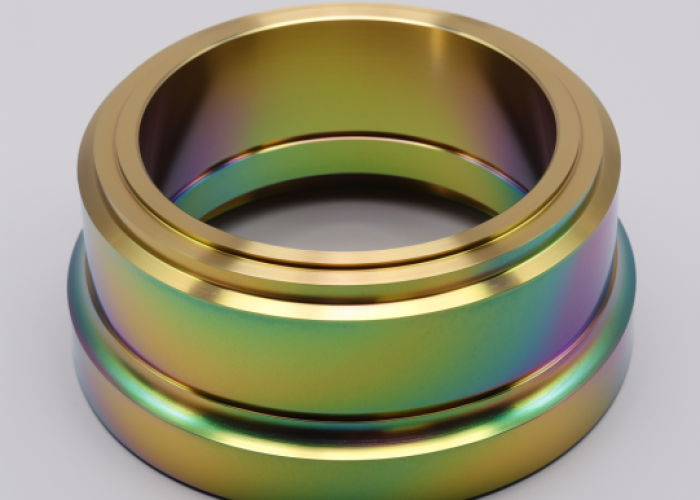
Does Alodine Coating Change CNC Part Dimensions?
Alodine coating adds only 0.5-4 microns to part dimensions—virtually negligible for most CNC applications and significantly thinner than anodizing (10-25 microns). This ultra-thin film preserves critical tolerances, threaded features, and assembly fits without requiring design modifications.
Dimensional Impact Comparison:
- Alodine coating: 0.5-4 microns (0.00002-0.00016 inches)
- Type II anodizing: 10-25 microns (0.0004-0.001 inches)
- Powder coating: 50-100 microns (0.002-0.004 inches)
- Standard CNC tolerances: ±0.005″ (±0.13mm) or looser – alodine has negligible impact
The coating thickness remains consistent across complex geometries, including internal threads, blind holes, and thin-wall sections. Unlike electrochemical processes that can create thickness variations, alodine’s chemical conversion produces uniform coverage regardless of part orientation or complexity.
For assemblies requiring precise fits, alodine coating eliminates the need for post-coating machining or tolerance adjustments. Press-fit bearings, threaded assemblies, and mating surfaces maintain their original specifications, reducing manufacturing complexity and cost.
Design Takeaway: Specify alodine coating on tight-tolerance CNC parts without dimensional concerns—the coating thickness is negligible compared to standard machining tolerances and won’t affect assembly or fit requirements.
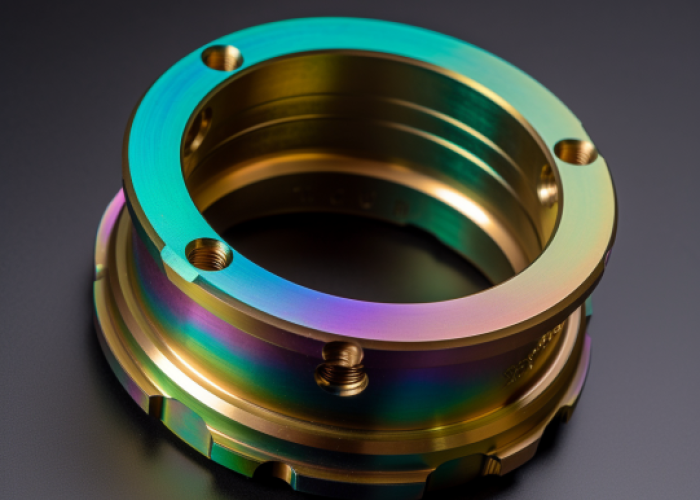
What Surface Finish Does Alodine Coating Provide?
Alodine coating produces a clear to golden-yellow surface finish with minimal texture change, maintaining the original machined surface appearance while adding corrosion protection. The coating preserves the underlying CNC surface finish without adding significant roughness or altering the part’s visual characteristics.
Alodine Surface Finish Characteristics:
- Visual appearance: Clear, iridescent, or golden-yellow depending on coating type
- Surface roughness: Minimal change to original Ra values (typically <0.1 μm increase)
- Texture preservation: Maintains original machined finish (brushed, bead blasted, etc.)
- Defect visibility: Underlying surface imperfections remain visible through coating
- Consistency: Uniform appearance across complex geometries and internal features
The coating follows the contours of the original surface rather than filling in or smoothing imperfections. Machined surfaces with Ra values between 0.8-6.3 μm retain their original finish characteristics after alodine treatment. This preservation is critical for sealing surfaces in hydraulic assemblies and optical components where surface texture directly affects functionality.
Salt spray testing demonstrates that alodine-coated surfaces maintain their appearance consistency over 500+ hours of exposure, with minimal color change or surface degradation. Visual inspection per MIL-DTL-5541 standards confirms coating uniformity, while surface profilometer measurements verify that Ra values remain within ±0.1 μm of the original machined finish.
Unlike powder coating or thick paint systems that can mask surface imperfections, alodine coating makes existing scratches, tool marks, or surface defects more visible due to its slight color change. This transparency requires careful surface preparation during machining to achieve the desired final appearance.
Design Takeaway: Plan your CNC surface finish before alodine coating—the coating preserves the original machined texture, so any desired smoothness or surface preparation must be completed during machining rather than relying on the coating to improve surface quality.
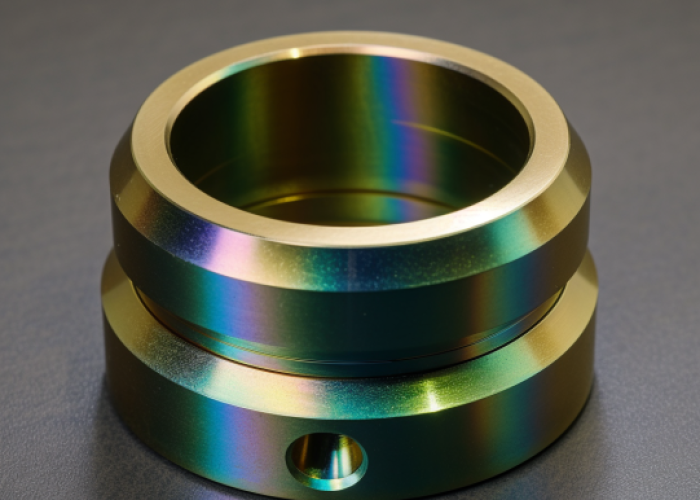
How Does Alodine Differ from Anodizing?
Alodine uses a purely chemical process while anodizing requires electrical current, resulting in different coating properties, costs, and applications. The fundamental difference lies in the process mechanism: alodine creates a conversion coating through chemical reaction, while anodizing builds up an oxide layer through electrochemical oxidation.
Key Process Differences:
- Alodine process: Chemical bath at room temperature, no electrical current required
- Anodizing process: Electrolytic bath with controlled electrical current and temperature
- Equipment needs: Alodine requires simple tanks; anodizing needs power supplies and controls
- Processing time: Alodine takes minutes; anodizing requires 30-60+ minutes
- Technical expertise: Alodine has simpler setup; anodizing demands specialized knowledge
Performance Comparison:
- Coating thickness: Alodine 0.5-4 μm vs anodizing 10-25 μm
- Durability: Anodizing provides superior wear and abrasion resistance
- Electrical properties: Alodine maintains conductivity; anodizing creates insulating layer
- Color options: Anodizing offers wide color range; alodine limited to clear/golden
- Corrosion protection: Both effective, but anodizing generally provides longer-term protection
Aerospace applications typically specify Type II anodizing for exterior structural components exposed to weather, while alodine coating is preferred for interior electrical assemblies requiring grounding continuity. Medical device manufacturers often choose alodine for enclosures where electrical safety standards mandate conductive paths, while anodizing is selected for patient-facing components needing durability and cleanability.
Both processes must meet specific industry standards: alodine follows MIL-DTL-5541 for military applications, while anodizing complies with MIL-A-8625 specifications. Salt spray testing per ASTM B117 validates corrosion performance for both finishes.
Design Takeaway: Choose alodine for electrical conductivity, paint adhesion, or tight tolerances; select anodizing for superior durability, wear resistance, or decorative appearance requirements.
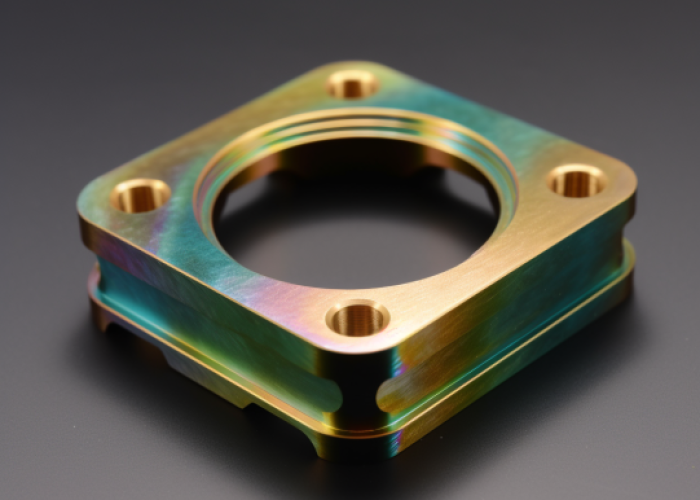
When Should You Use Alodine Instead of Anodizing?
Choose alodine when your application requires electrical conductivity, minimal dimensional change, or serves as a paint base—particularly for precision assemblies where tolerances are critical. Alodine excels in applications where anodizing’s thickness or insulating properties would compromise functionality or assembly requirements.
Alodine is Preferred When:
- Electrical conductivity required: Grounding paths, EMI shielding, electrical enclosures
- Tight tolerances critical: Parts with ±0.002″ or tighter specifications
- Paint base needed: Superior adhesion for subsequent coating systems
- Complex geometries: Internal channels, blind holes, intricate CNC features
- Cost sensitivity: Budget-conscious projects requiring basic corrosion protection
Anodizing is Better For:
- High wear applications: Moving parts, sliding surfaces, frequent handling
- Decorative requirements: Color matching, aesthetic appearance, consumer products
- Harsh environments: Outdoor exposure, chemical contact, extreme temperatures
- Thick protection needed: Long-term corrosion resistance in severe conditions
Medical device manufacturers typically specify alodine for electronic enclosures requiring EMI shielding and electrical grounding, while choosing anodizing for patient-contact surfaces needing durability and cleanability. Aerospace applications use alodine for avionics housings where electrical continuity is mandatory, but specify anodizing for structural components exposed to weather and mechanical stress.
Audio equipment manufacturers prefer alodine for amplifier chassis and faceplates where electrical grounding is essential for signal quality, while anodizing is selected for control knobs and handles requiring wear resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Design Takeaway: Select alodine when electrical function, tight tolerances, or paint adhesion drive your requirements; choose anodizing when durability, appearance, or harsh environment exposure are primary concerns

How Much Does Alodine Coating Cost Compared to Anodizing?
Alodine coating typically costs 30-50% less than anodizing due to simpler processing requirements, faster cycle times, and lower equipment needs. The cost advantage stems from room-temperature chemical baths versus anodizing’s electrical systems, temperature control, and longer processing cycles.
Cost Factors Comparison:
- Processing time: Alodine 5-15 minutes vs anodizing 45-90 minutes
- Equipment investment: Alodine requires basic tanks; anodizing needs power supplies and controls
- Energy consumption: Alodine minimal vs anodizing significant electrical usage
- Labor requirements: Alodine simpler setup vs anodizing technical expertise needed
- Batch efficiency: Alodine handles mixed part sizes easily; anodizing requires current density calculations
Typical Cost Ranges (per square foot):
- Alodine coating: $0.50-$1.50 for standard parts
- Type II anodizing: $1.00-$2.50 for clear finish
- Colored anodizing: $1.50-$3.00 depending on color requirements
- Setup costs: Alodine minimal; anodizing requires rack design and current calculations
Volume significantly impacts pricing for both processes. Small prototype runs favor alodine due to minimal setup requirements, while large production volumes can reduce anodizing’s per-part cost through economies of scale. Lead times also differ: alodine coating often ships within 3-5 days, while anodizing typically requires 7-14 days due to process complexity and scheduling.
For precision CNC parts requiring secondary operations, alodine’s dimensional stability eliminates post-coating machining costs that anodizing sometimes requires. This hidden cost advantage can offset anodizing’s higher processing fees, especially for tight-tolerance assemblies.
Design Takeaway: Factor total project cost including lead time, secondary operations, and tooling requirements—alodine’s lower processing cost and faster turnaround often provide better overall value for applications not requiring anodizing’s specific performance advantages.
Conclusion
Alodine coating offers excellent corrosion protection with minimal dimensional impact, making it ideal for precision CNC aluminum parts requiring electrical conductivity or paint adhesion. Choose alodine over anodizing when tight tolerances, cost efficiency, or electrical functionality drive your design requirements. Contact us to explore manufacturing solutions tailored to your alodine coating requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Standard CNC tolerances (±0.005″ or ±0.13mm) work perfectly with alodine coating. The 0.5-4 micron coating thickness has negligible impact on dimensions, so no tolerance adjustments are needed for most precision applications.
Yes, alodine coating maintains aluminum’s electrical conductivity unlike anodizing which creates an insulating layer. This makes alodine ideal for grounding applications, EMI shielding, and electrical enclosures requiring conductive paths.
Alodine coating typically adds 3-5 days to standard CNC lead times. The fast chemical process (5-15 minutes) allows quick turnaround compared to anodizing which often requires 7-14 days due to process complexity.
Post-coating machining removes the protective film and isn’t recommended. All CNC machining, drilling, and threading should be completed before alodine application to maintain corrosion protection and surface integrity.
Yes, alodine significantly improves paint adhesion compared to bare aluminum. The chemically bonded surface provides superior primer and paint attachment, reducing coating failures like chipping or flaking in demanding applications.
Yes, alodine’s ultra-thin film preserves thread fit and function without dimensional interference. Unlike anodizing, threads maintain proper engagement and torque specifications after coating application.