In this article, we’ll compare the two processes to help you decide which is best suited for your project.
Table of Contents
Overview of CNC Machining
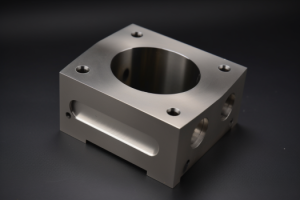
CNC machining is a reliable and precise method that utilizes computer-controlled machinery such as lathes, mills, and routers to create complex components for various aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors.
The process involves cutting tools guided by carefully programmed computers that precisely and accurately deliver the required shape, size, and finish.
Process
The CNC machining process typically involves the following steps:
- Design: To begin the process, utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to develop a digital representation of the part or component you wish to manufacture.
- Programming: Upon completing the digital design, a CNC programmer utilizes software designed to generate an automated program that commands the machine to produce parts from raw material.
- Setup: Loaded with the raw material, the CNC machine mounts cutting tools to beginning machining – removing materials according to programmed instructions. The tooling can move in various directions, including up-down, left-right, or back and forth.
- Finishing: Following the completion of machining, the finished product is removed from its CNC machine and may need additional finishing processes such as polishing or coating.
Applications
For industries that require precision parts, CNC machining is the go-to solution.
Automotive, aerospace, and medical are just a few of such fields that benefit from this technology.
From rapid prototyping to creating intricate components with high accuracy – some distinct advantages of using CNC machining for various applications include:
- Manufacturing of engine parts, such as cylinder heads and crankshafts.
- Creation of molds and dies used in producing plastic and metal parts.
- Production of medical implants, such as hip and knee replacements.
- Creation of custom-designed parts for specialized machinery or equipment.
There’s no denying the precision, repeatability, and versatility that CNC machining can offer.
Yet, for smaller manufacturing runs especially, it may cost more than other production processes.
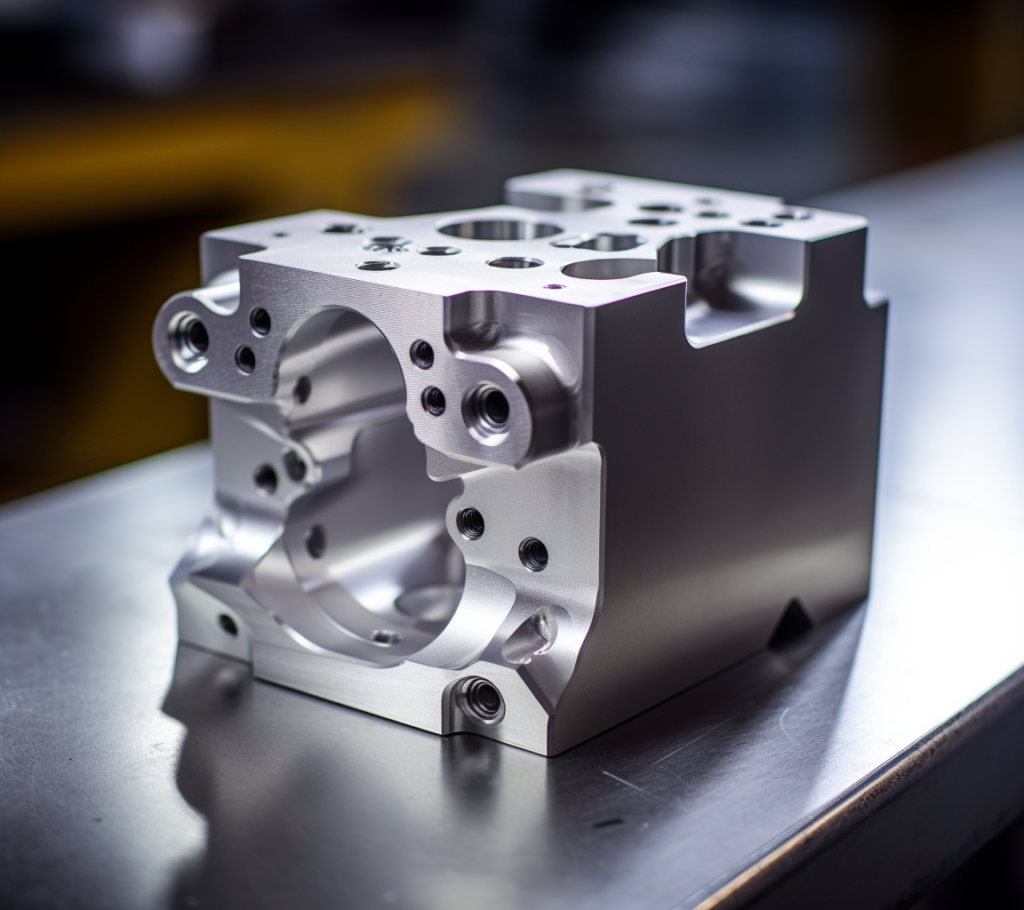
Overview of 3D Printing
Unleash the power of 3D Printing or additive manufacturing with a click. By examining digital files and stacking layers of diverse materials such as plastics, metals, and ceramics to construct three-dimensional objects effectively, this inventive process allows us to fashion intricate designs that are inconceivable through traditional techniques!
The 3D printing process typically involves the following steps:
- Design: The first step is to create a digital model of the object to be produced using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Slicing: The digital model is then sliced into multiple layers and converted into machine-readable instructions for the 3D printer.
- Printing: The 3D printer builds the object layer by layer, adding material until the final product is complete.
- Finishing: Once the Printing is complete, the object may require additional finishing operations such as sanding or painting.
Applications
Industries such as product design, architecture, and jewelry need rapid prototyping solutions –
that’s where 3D Printing comes in. From its use cases to large-scale applications, here are some of the ways 3D Printing works:
- Creation of complex geometries, such as organic shapes and lattice structures that would be difficult to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
- Rapid prototyping of products for design testing and validation.
- Production of customized products, such as prosthetic limbs and dental implants.
- Creation of architectural models and sculptures.
The advantages of 3D Printing are numerous – from its ability to create intricate shapes and designs to minimal setup costs, quick prototyping, and beyond.
However, it has some drawbacks regarding the strength and longevity of materials used; as such, there may be better methods for producing large numbers of parts requiring high endurance levels.

Comparison of CNC Machining and 3D Printing
Before you choose between CNC machining and 3D Printing, it’s important to evaluate several components.
To help guide your decision-making process, here is a comparison of the two technologies regarding material compatibility & limitations, precision & accuracy, cost efficiency & production volume, and lead time & sustainability impact.
Material Compatibility and Limitations
CNC machining offers versatility, accommodating various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. In comparison, the scope of 3D Printing is far more restrictive – primarily limited to plastics, resins, and select metals.
Moreover, while CNC machining can generate parts with enhanced durability ideal for high-stress projects, 3D Printing may need better strength or longevity due to its material restrictions.
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machining is unequaled in its precision and accuracy, delivering results with an astounding tolerance level of up to 0.0001 inches. 3D Printing reaches different levels of exactitude;
however, it can manufacture complex geometries that are either difficult or impossible to achieve when using traditional CNC machining techniques.
Its tolerances usually range from 0.001 -0.005 inches, showcasing remarkable versatility while providing high-quality parts and products.
Cost Considerations
Due to its extensive setup time and specialized machinery, CNC machining can be expensive for small production runs.
3D Printing is a more cost-effective alternative for such cases; it has low setup costs, so you’ll save money as there is no need to invest in costly equipment.
Nonetheless, your goal is the mass production of parts. In that case, the expenditure on each piece with 3D Printing could surpass that of CNC machining—making it better suited for rapid prototyping or short series manufacturing tasks only.
Production Volume and Lead Time
For moderate to large-scale manufacturing, CNC machining is the way to go; it typically takes several days to a few weeks before production is complete.
If you need quick prototyping or small batch runs, 3D Printing should do the trick. Its lead time ranges from only hours up until several days.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
CNC machining can lead to significant excess material that must be recycled or disposed of correctly.
At the same time, 3D Printing produces less waste but likely requires more energy for parts production since heat is necessary to liquefy and fuse the elements.
Ultimately, deciding between CNC machining and 3D Printing comes down to the individual application’s needs; each has advantages and drawbacks.
When determining the best fabrication process for your project, CNC machining offers unparalleled precision and accuracy.
However, 3D Printing may be more cost-effective if you require rapid prototyping or complex geometries.
When deciding between these two processes, it is also essential to consider factors such as production volume and environmental impact.
Future Developments and Advancements
As CNC machining and 3D printing advance rapidly, exciting new possibilities arise. Here are some potential future developments for these two cutting-edge technologies:
- Hybrid Technologies: The integration of CNC machining and 3D printing technologies can be a match made in heaven. Hybrid machinery allows you to use the benefits of both techniques; where 3D Printing is perfect for producing intricate shapes, CNC machining quickly takes care of post-processing and finishing tasks.
- Multi-Material Printing: Materials currently used in 3D Printing are limited, but innovations in material science could expand the range of materials available. From metals to ceramics and composites, multi-material 3D Printing allows us to manufacture parts that have more intricate properties. Therefore, this type of technology has great potential for creating components with evermore complex characteristics.
- AI: 3D Printing and CNC machining have the potential to be revolutionized by AI and Machine Learning algorithms to increase precision and reduce waste, making production more efficient. By adjusting processes in real-time, intelligent machines could ensure optimal efficiency during all manufacturing or printing stages.
- Sustainability: To reduce their environmental footprint, 3D Printing and CNC machining must look towards innovative possibilities such as conserving energy, reusing waste products, and embracing renewable power sources. By doing so, these modern technologies can be more sustainable while continuing to drive progress forward.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: On-demand manufacturing is becoming increasingly accessible thanks to digital design tools and cloud computing, enabling rapid production of customized components and goods. Providing a more efficient alternative could significantly reduce reliance on large-scale manufacturing runs.
Conclusion
All in all, CNC machining and 3D Printing are reliable manufacturing technologies with advantages and disadvantages.
CNC machining offers unparalleled accuracy, precision, and the ability to work with a wide selection of materials, whereas 3D Printing is ideal for creating intricate designs quickly.
It’s essential to consider factors such as material compatibility, cost-effectiveness, production volume requirements,
and sustainability issues when deciding between these two processes.
Technology is evolving rapidly, and CNC machining and 3D Printing will likely become more complementary.
These advancements make potential enhancements to precision, sustainability, and on-demand manufacturing capabilities possible.
Hybrid solutions that take advantage of both technologies’ best aspects could soon be developed – truly creating something remarkable!
FAQS
Lead times depend on some factors, including size, complexity, and quantity. Generally speaking, CNC machining has faster lead times since it does not require time for post-processing, whereas 3D Printing requires longer lead times due to the printing process itself and any additional post-processing required.
Post-processing for CNC machining typically involves deburring and sanding, while 3D Printing requires additional steps such as support removal, surface finishing, and painting. Heat treatment or welding may also be needed depending on the application.
It depends on the application and requirements. Generally speaking, 3D Printing is more cost-effective for low volumes or complex geometries, while CNC machining is better suited for larger batches with less intricate designs.
CNC machining typically uses metals such as steel and aluminum and plastics like ABS and polypropylene. 3D Printing supports various materials, including thermoplastics, metals, composite filaments, elastomers, and wax.
CNC machining is ideal for creating complex parts with precise accuracy, making it great for producing prototypes or low-volume production runs. 3D Printing, on the other hand, is well suited for paying large batches quickly and cost-effectively with minimal waste material. Additionally, 3D Printing can produce parts with interior features and geometries that are impossible to achieve with CNC machining.