What is CNC machining?
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process similar to a robot. Applying the software, dimensional tasks are removing layers of material from a blank (or workpiece) and producing custom plastic and metal parts.

Introduction
The CNC Machining process can produce parts with tight tolerances and excellent material properties in the end. The high level of repeatability of this manufacturing process makes it suitable for not only prototypes but also high-volume custom parts production.
This introductory guide will overview the basic principles and mechanics of one of the most common manufacturing processes today.
Table of Contents
How does CNC Machining work?
A CNC machine can be a milling machine, a turning machine, a touter, or an EDM machine. There are two main types of CNC (Computer numerical control) machining systems: Milling and turning. Aside from being unique, they can also be used to manufacture various geometries.
Let’s talk about Milling and turning. A closer look at these two machine setups and how parts are manufactured shows how each is utilized differently.
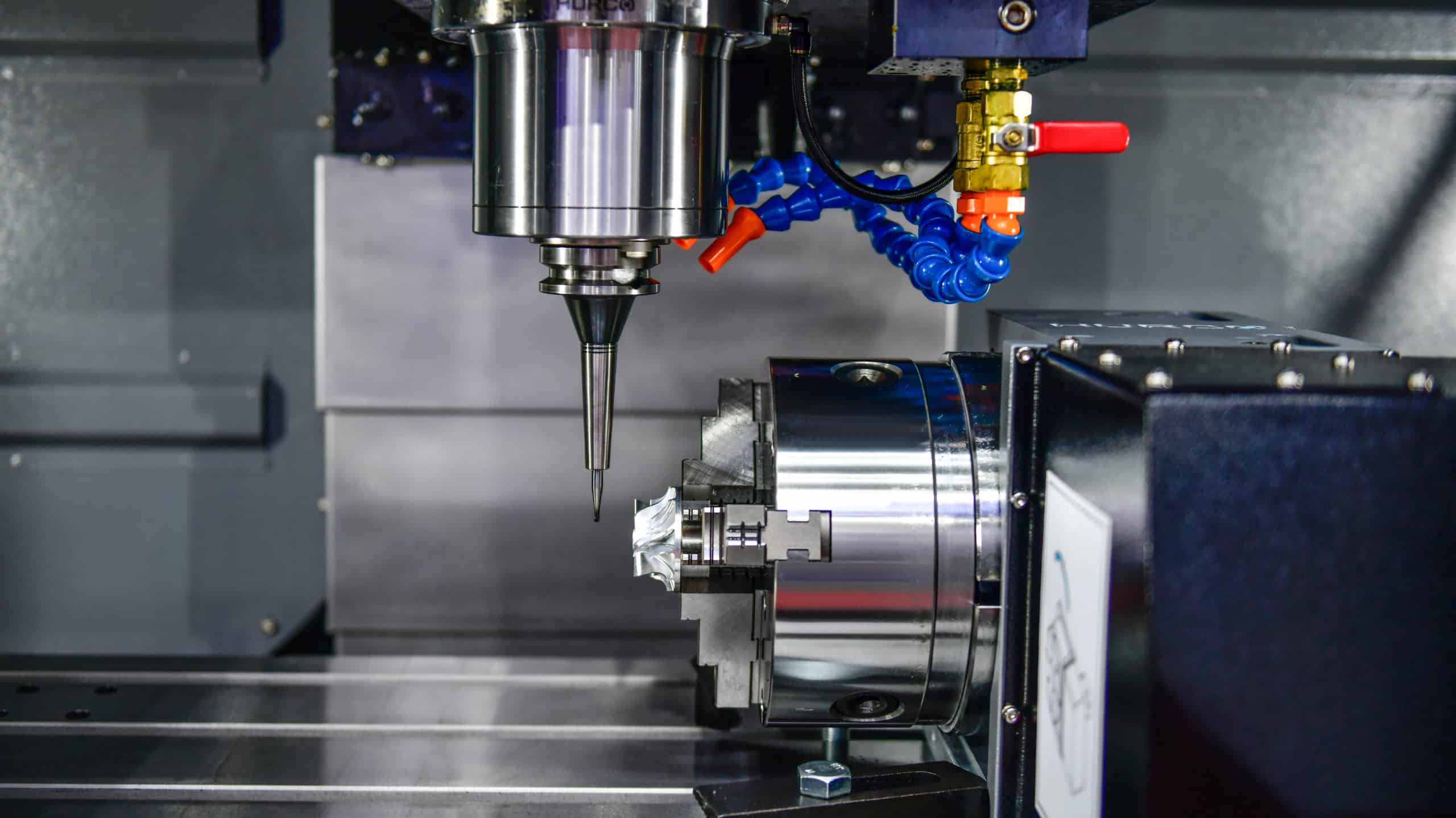

How does CNC Milling work?
Material is removed from an object using rotary cutters in milling machines. Materials can be drilled, bored, and cut. The material is removed along tool axes by milling machines during this process. Different types of milling machines are used in many industries.
The types of milling machines
- Bed Type Milling Machine
- CNC Milling Machine
- C-Frame Milling Machine
- Column Milling Machine
- Drum Milling Machine
- Duplex Milling Machine
- Horizontal Milling Machine
- Ram-type Milling Machine
- Rotary Table Milling Machine
- Simplex Milling Machine
- Turret Milling Machine
- Triplex Milling Machine
- Tracer Controlled Milling Machine
- Universal Milling Machine
- Vertical Milling Machine
Among all these milling architectures, the CNC machine is the most popular, which utilizes rotating cutting tools to remove material from parts fixed, mounted, or moved/positioned by the machine bed.
What are the most common cutting tools of CNC Milling?
Creating a variety of geometries, CNC milling machines employ a wide variety of Cutting tools. This section will discuss some of the most commonly used milling tools. Each type has a different purpose and uses case. Take a look at the possibilities.
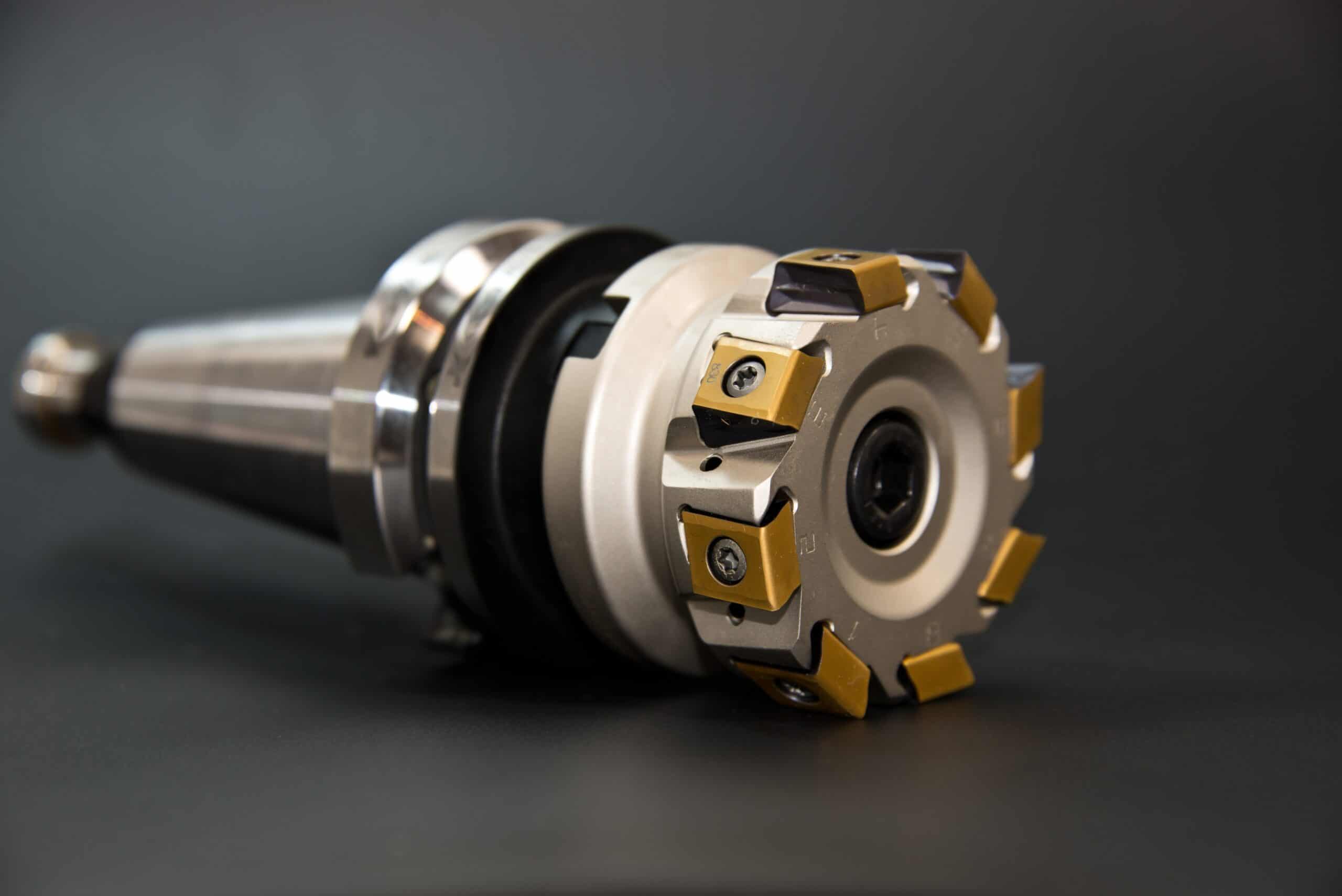

CNC Milling cutting tools can be divided into five types for cutting purposes.
Type 1:Cutters Type 2: Drills Type 3: Threading
Type 4: Taps Type 5: End mills.
Cutters Type
Cutters, Such as Ball cutters, Fly cutters, Cross cutters, and face cutters. It is usually used to remove large amounts of material from the workpiece to reduce the time necessary for the next machining operation.
Drills Type
Drills are designed to drill through parts and then side mill grooves or shapes. The versatility of these machines makes them popular in milling manufacturing. Their applications range from drilling to spotting to chamfering to countersinking.
Threading Type
Threading taps, workpieces are threaded with threading taps. High-speed milling centers equipped with rigid taps can thread holes faster than thread milling. More complex materials, such as steel, can also be threaded with tapping.
End mills
End mills, instead of drills, can cut in any direction. Among the applications of endmills are contouring, drilling, face milling, profile milling, plunging, reaming, slotting, and tracer milling.
How does a CNC Milling Machine work?
How does a CNC Milling machine work? Using a rotating cylindrical cutter, a CNC milling machine creates slots, holes, and details in material that can be used to turn it into a mechanical component or vehicle. Three to five axes are typically used in most machines, resulting in higher precision and detail.
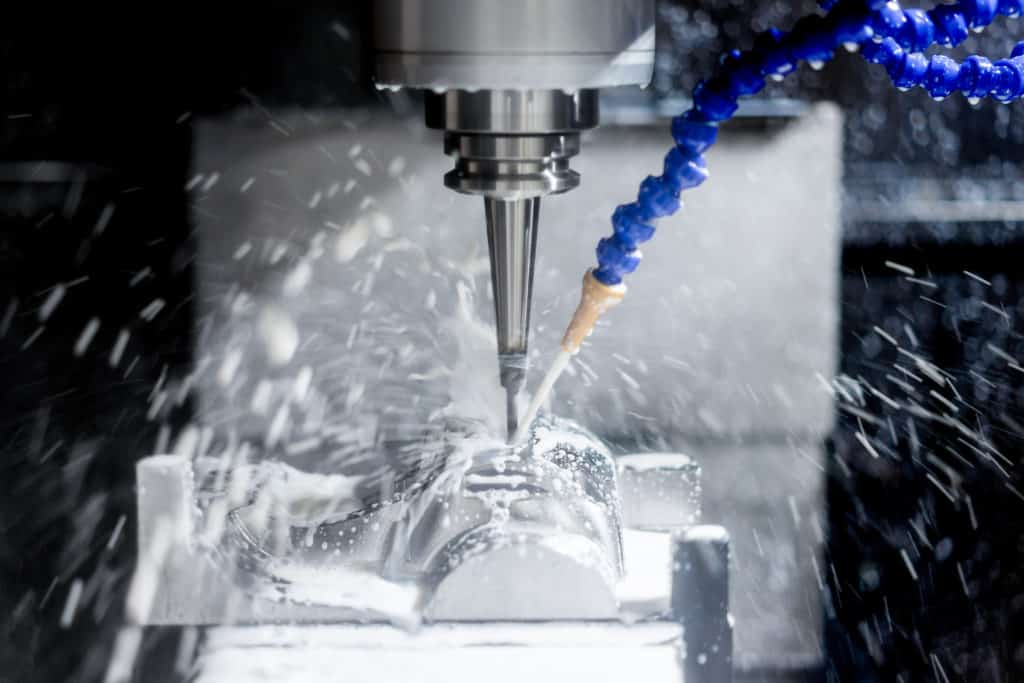

CNC Milling machine working steps
Most CNC Milling machines/systems have three linear degrees of motion: the X, Y, and Z axes. Machines with advanced features may feature a 4th and 5th rotational axis, making it possible to machine more exact shapes by rotating the bed or the tool head ( A & B axes).
Here are the 7-steps that a CNC Milling machine manufacturing parts.
1. Technical drawing / CAD drawing
Engineers and mechanics depend on a technical drawing to communicate a detailed representation of a part manufactured in two or three dimensions. It contains essential manufacturing data, such as distances, dimensions, shapes, sizes, colors, and surfaces.
2. CAD models Convert into CNC programs
By using G-code, the operator converts CAD models into CNC commands.
3. CNC Milling Machine setup
The milling machine should be equipped with specialized cutting tools and set up correctly.
4. The aligned workpiece
A blank is also known as a block of material. Make sure the workpiece is aligned and precisely positioned on the machine bed.
5. The milling operation
It’s all set now. All you have to do is press the button to start the process.
6. Repeat steps
Flipping the workpiece if the operator cannot reach certain features with a single setup is necessary.
7. Part deburr
After completing these steps, the operator would pull out the milling part and manually deburr those sharp edges
8.Part dimensions inspect
Dimension inspection follows. Before sending out for the next step, every structure and size must be checked, including taps, slots, recesses, pockets, and holes.
9. Part post-processing
Chemical treatment or hardening may be required on some custom parts to improve their surface and strength.
CNC Milling parameters
In this section, let’s focus on the size of machining that can be workable and the accuracy that can be achieved. The dimensions that CNC milling systems can work with on both metals and plastics.
| 3-Axis Milling | ||
| Size | Metals | Plastics |
| Maximal size | 360*360*100mm | 360*360*50mm |
| Minimal Diameter | 0.30mm | 0.50mm |
| 4-Axis Milling | ||
| Size | Metals | Plastics |
| Maximal size | 120*80*50mm | 120*80*50mm |
| Minimal Diameter | 0.50mm | 0.50mm |
| 5-Axis Milling | ||
| Size | Metals | Plastics |
| Maximal size | 600*600*300mm | 600*600*300mm |
| Minimal diameter | 0.50mm | 0.50mm |
Our system typically considers the part accuracy under ISO2768 if the tolerance is not specified in the technical drawing. You can find the tolerance chart here.
ISO2768 tolerance table
| Size Range | Metals | Plastics |
| 0.5mm – 30mm | 0.020mm | 0.050mm |
| 30mm – 120mm | 0.050mm | 0.10mm |
| 120mm – 300mm | 0.10mm | 0.150mm |
| 300mm – 600mm | 0.20mm | 0.30mm |
How does CNC Turning Work?
How does CNC Turning Work?
CNC turning, also known as CNC Lathe, is a subtractive manufacturing method in which material is removed by rotating material rods against held cutting tools. Asymmetrical parts can be manufactured this way using the CNC Turning method. Compared to milled parts, turned parts are typically more cost-effective and faster to produce.
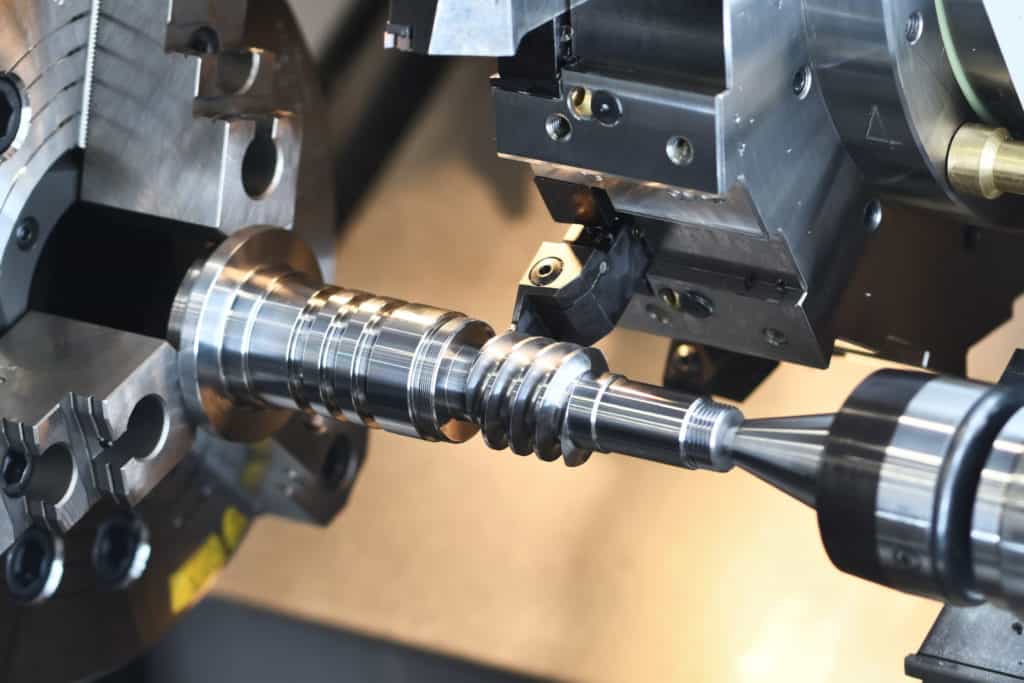

What are the CNC Turning machine working steps
The following is an overview of how a CNC turning machine manufactures parts.
1. Technical drawing / CAD drawing
To begin with, CNC Turning also requires CAD drawings, just as CNC Milling does.
2. CAD models Convert into G-Code
Based on the CAD model, a G-CODE is generated so the machine can understand the instructions.
3. Load blank material
Make sure the part is loaded securely into the chunk.
4. Select and load your tooling
Cutting tools are required for different structures of workpieces. Ensure the machine has the right tool Before executing the program.
5. Execute the program
6. Repeat steps
Flip / move the part and repeat this step. Otherwise, once the turned part is finished cutting the material, it can be further processed.
7. Part deburr
8. Part dimensions inspect
9. Part post-processing
What are the most common cutting tools for CNC Turning?
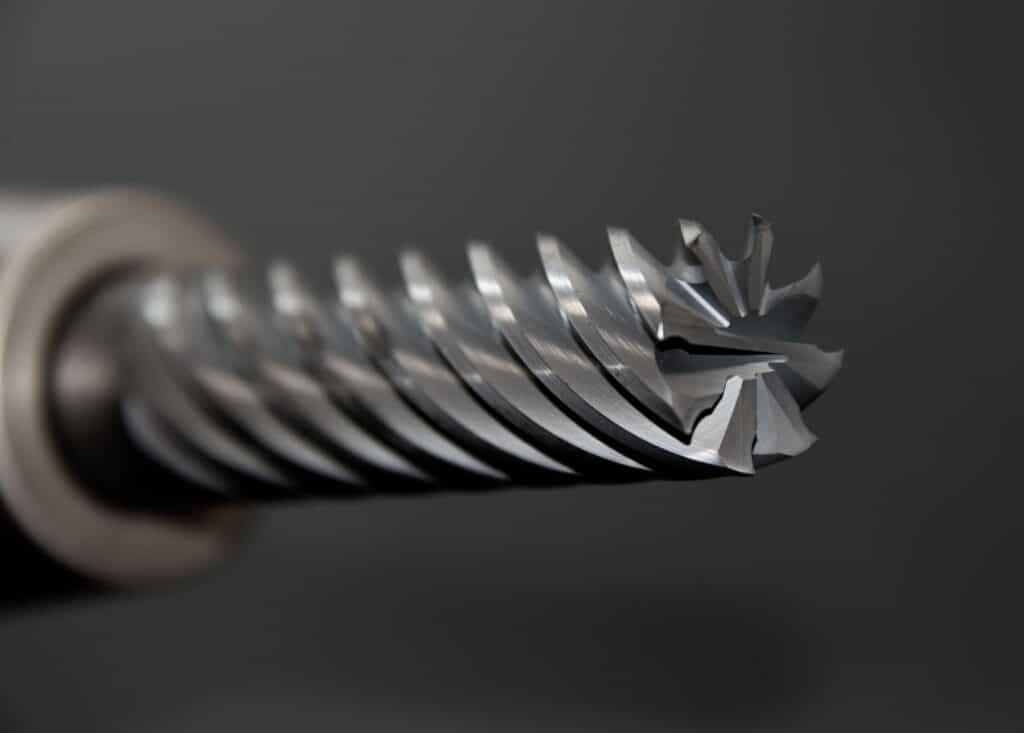

Consideration factors before choosing tools
Programming feeds and speeds adequately begin with choosing the right cutting tool.
The 7 factors need to be considered before making the decision.
- Machine condition
- Workpiece material class and condition
- Workpiece diameter
- Type of cut
- Depth of cut
- Cutter material
- Cutter geometry
Cutters, Such as Ball cutters, Fly cutters, Cross cutters, and face cutters. It is usually used to remove large amounts of material from the workpiece to reduce the time necessary for the next machining operation.
How many types of CNC Turning tools for projects?
There are 9 types of Cutting tools for CNC Turning projects
- Type 1: Boring Tool
- Type 2: Chamfering Tool
- Type 3: Facing Tool
- Type 4: Forming Tool
- Type 5: Grooving Tool
- Type 6: Knurling Tool
- Type 7: Parting Tool
- Type 8: Thread Cutting Tool
- Type 9: Turning Tool
Type 1: Boring Tool.
A boring tool can enlarge an already drilled or cast hole to a specific diameter. It’s often preferable to drilling because of its accuracy, and it comes in many forms.
Type 2: Chamfering Tool
An essential tool for machinists is the chamfer tool or chamfer cutter. Chamfer mills eliminate sharp edges and leave chamfers instead. It will result in a more substantial and more aesthetically pleasing part.
Type 3: Facing Tool
The facing tool is used to refine materials and achieve superior surface finishes. Their wide cutting edges are designed for fast feed rates and high spindle speeds, enabling them to remove skim coats quickly and effectively.
Type 4: Forming Tool
The forming tool is a cutter to shape irregular contours such as curves and straight lines.
Type 5: Grooving Tool
External and face grooving are two types of grooving to create a narrow cut in the workpiece.
Type 6: Knurling Tool
On a lathe machine, a knurling tool is used for manufacturing and repairing purposes. Knurling tools are used to give the metal a cris-cross pattern shape, which is easier for a human hand to grasp. Knurling tools generate three common patterns: diagonal, diamond, and straight.
Type 7: Parting Tool
The parting tool is more like a grooving tool. Only the slot is deeper.
Type 8: Thread Cutting Tool
Threading is done with the help of taps and dies, which are tools for creating screw threads. Most of these tools are cutting tools, while others are forming tools. Cutting or forming the female portion of the mating couple with a tap is necessary.
Type 9: Turning Tool
Turning tools are applied to cut a single point on a workpiece with a rotating tool or machined surface, which are used on lathes to finish outside diameters.
what are the CNC Turning parameters?
In this section, let’s focus on the size of machining that can be workable and the accuracy that can achieve.
The dimensions that CNC turning systems can work with on both metals and plastics.
| Size | Metals | Plastics |
| Maximal machined size | 800*800*600mm | 600*600*300mm |
| Minimal machined size | 0.050mm | 0.10mm |
Our system typically considers the part accuracy under ISO2768 if the tolerance is not specified in the technical drawing. You can find the tolerance chart here.
Metals
| Nominal size | Linear Dimensions | Angular Dimensions | External Radius & Chamfer Heights |
| 0.5mm to 3mm | ±0.05mm | ±1° | ±0.20 |
| > 3mm to 6mm | ±0.05mm | ±0°30′ | ±0.50 |
| > 6mm to 30mm | ±0.10mm | ±0°20′ | ±1.0 |
| > 30mm to 120mm | ±0.15mm | ±0°10′ | |
| > 120mm to 400mm | ±0.20mm | ±0°5′ | |
| > 120mm to 400mm | ±0.30mm | / | |
| > 120mm to 400mm | ±0.50mm | / |
Plastics
| Nominal size | Linear Dimensions | Angular Dimensions | External Radius & Chamfer Heights |
| 0.5mm to 3mm | ±0.10mm | ±1° | 0.02 |
| > 3mm to 6mm | ±0.10mm | ±0°30′ | 0.02 |
| > 6mm to 30mm | ±0.20mm | ±0°20′ | 0.05 |
| > 30mm to 120mm | ±0.30mm | ±0°10′ | 0.1 |
| > 120mm to 400mm | ±0.50mm | ±0°5′ | 0.2 |
| > 400mm to 1000mm | ±0.50mm | / | 0.3 |
| > 1000mm to 2000mm | ±0.80mm | / | 0.4 |
What are the available materials for CNC Machining?
Choosing suitable materials is crucial when designing a CNC machined part. Following are the basic steps we recommend when selecting your custom parts’ materials.
3 Steps to choosing the suitable materials for your custom parts

1.Determine the material requirements, including mechanical, thermal, and other material requirements, as well as cost and finish. It’s critical to take into account how your parts will be used and what type of environment they’ll be exposed to.
2.Determine a few materials that could meet your design requirements and pinpoint a few that could fulfill all or most of them.
3.Choose the material that will fulfill the design requirements – usually, a compromise is required between mechanical performance and cost.
Here’s an overview of the materials and cost.
| Metals | Plastics | ||
| Material | Price | Materials | Price |
| Aluminum 6061 | 30 | POM | 30 |
| Aluminum 7075 | 80 | ABS | 18 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 85 | Nylon 66 | 30 |
| Steel 45 | 25 | PVC | 20 |
For CNC machining, what are the standard blank sizes?
An initial piece of material loaded onto a CNC machine is called a blank. Plates are available in a variety of sizes as stock materials. Here are some standard blank dimensions you might find in a typical machine shop, summarized in the tables below.
| Types | Plate | Rods |
| Thickness | Diameter | |
| 3 mm | 3 mm | |
| 4 mm | 4 mm | |
| 5 mm | 5 mm | |
| 6 mm | 6 mm | |
| 7 mm | 7 mm | |
| 8 mm | 8 mm | |
| 9 mm | 9 mm | |
| 10 mm | 10 mm | |
| …. | …. | |
| 200 mm | 200 mm |
Recommended materials for Rapid prototyping Service
The key to rapid prototyping is speed. We can provide CNC machined parts in 48 hours or less. In order to achieve that, Aluminum alloy and POM are the most recommended materials for rapid prototyping service; there are reasons for those recommendations.

Aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloys have excellent properties with high thermal conductivity, high strength-to-ratio, and high corrosion resistance. Production prototypes and other types of parts are often the most economical option because they are easy to machine and cost-effective in bulk.
Let’s break down aluminum alloys into their different types.
Aluminum 6061
It has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and is one of the most popularly used aluminum alloys.
6082 aluminum
6082 aluminum has similarly composed and material properties as 6061 aluminum, which is why 6082 is more commonly used in the United States and Europe.
Aluminum 7075
In aerospace applications, aluminum 7075 is the most commonly used alloy for reducing weight. Due to its excellent fatigue properties and heat-treating capability, it is comparable to steel in terms of strength and hardness.
POM
As plastics are prone to melting and bending during machining, their machinability is primarily determined by their thermal properties and stiffness. Among plastics, POM is the easiest to machine.
What surface are finishes available for CNC machining?
CNC Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that can produce parts with tight tolerance and fine details from an enormous range of metals and plastics. CNC’s subtractive nature, however, often leaves visible marks on the parts that come off milling and turning machines.
What surface are finishes available for CNC machining? You can apply As machined, Anodizing, Electroplating, and . Powder coating.
Surface finishing plays a vital role in this process. CNC machine parts can improve their surface roughness, cosmetic and visual properties, as well as their wear resistance by applying suitable surface finishes and post-processing. Correctly applied surface finishing improves functionalities and aesthetics, and in many cases, both.

How many heat treatments available for CNC Machining?
It is known that to dramatically improve key physical properties of metal alloys through heat treatments, such as hardness, strength, or machinability. Microstructures and chemical compositions of the material are modified, resulting in these changes.
Annealing, case hardening, carburizing, precipitation hardening, quenching, stress relieving, and tempering can be applied to CNC machining parts. Metal alloys can undergo heat treatment as part of the manufacturing process, usually before CNC Machining or after CNC Machining.
Annealing
A high temperature is applied to the metal during Annealing, and then it is slowly cooled to achieve the desired microstructure. This is usually applied after forming to improve machinability and soften metal alloys. The manufacturing process is used for most CNC machined parts if another heat treatment is not specified. Producing parts in this manner ensures that their mechanical properties are consistent.
Case Hardening
The case hardening process produces parts with a high hardness on the surface but soft underlines. It is often preferred to increase the hardness of the part throughout its volume rather than increasing its hardness throughout its volume.
Carburizing
Heat treatments such as carburizing are the most common method of case-hardening. This method involves heating mild steel to a high temperature in a carbon-rich environment, followed by quenching to lock in carbon. In the same way that anodizing increases the surface hardness of CNC aluminum parts, this increases the surface hardness of steel.
Precipitation hardening
As a three-step process, precipitation hardening involves first heating a material to a high temperature, then quenching it, and finally heating it to a high temperature for a long time. It dissolves and distributes uniformly in the metal matrix alloy elements that initially appear as discrete particles.
Quenching
During quenching, the material is heated to a very high temperature and then rapidly cooled in a liquid or air stream, usually oil or water when a material is cooled quickly, its microstructure changes when heated and locked in resulting in parts with high hardness.
stress relieving
To relieve residual stresses created during CNC machining, stress relieving involves heating the part to a high temperature. Doing so can produce parts with a more consistent mechanical property.
Tempering
Tempering reduces the brittleness of mild steel such as 1045 and A36, and alloy steels AISI 4140 and AISI 4240 by heating them at a lower temperature than annealing.
Ready to make your parts?
How to prepare Technical drawings for CNC Machining?
Designers, engineers, product developers, and machinists communicate technical requirements more effectively via technical drawings. It is possible to source better parts and cut costs by providing a technical drawing.
7 steps to prepare technical drawings for CNC Machining
- Draw the most critical views in the center, allowing enough space between them to add dimensions.
- Consider adding section details view if your part has complex internal features.
- add construction lines to all views
- Add the most important dimensions to your drawing
- specify the location, size, and length of all threads.
- add tolerance to your drawing.
- Fill all necessary info into the title block
Tips to reduce CNC Machining cost
Whether you want to create a single prototype or go into mass production, reducing manufacturing costs is often the top priority in CNC machining. It is, fortunately, possible to keep prices low by making design decisions. Design for machinability rules can help you produce affordable parts that still meet function design specifications.
- The following factors determine the cost of a CNC machined part:
- Machining time
- Start-up costs
- Material cost
- Other manufacturing costs
- Post-processing or surface finishing cost
Machining time
For large-scale production, simple design errors can hurt economies of scale due to the time spent on machining parts. The more time spent on machining a piece, the more expensive it becomes.
Start-up costs
Start-up costs are significant for small volumes due to the preparation of CAD files and process planning. They are also fixed, which is a blessing. The unit price can be lowered by applying large-scale principles if the design and surface finish are suitable.
Material cost
Generally, the cost of CNC machines is greatly influenced by the price and ease of machining bulk materials. The cost of your design can be reduced by optimizing it while carefully considering your materials.
Other manufacturing costs
It may be necessary to use special tooling, have close quality control, and operate at low speeds during the machining process to define tight tolerances or design parts with complicated features, which also affects the cost and time of manufacturing.
Post-processing

What are the characteristics of CNC machining?
There are some drawbacks to CNC machining, ranging from prototyping to mass-production of end-use parts, despite its viability and even idealization for many applications.
Precision and repeatability are excellent features of CNC machining. CNC is ideal for high-end applications like aviation and automotive, as Milling and turning can produce parts with very tight tolerances. It is suitable for most engineering applications to use materials that have excellent isotropic physical properties.
Here is an overview of the six advantages of CNC Machining.
- High Machining accuracy,
- High Replicated. Let the machine do the same cut over and over again.
- High production scalability.
- The high degree of automation, less labor intensity
- Good flexibility and versatility.
- High Consistent
Despite these benefits, CNC Machining is an expensive or even impossible option for specific geometric geometries because of its beautiful nature.
Frequently asked questions
- CNC Turning & CNC Lathes machines.
- CNC Electrical Discharge Machines.
- CNC Milling Machines.
- CNC Laser Machines.
We have them all in our manufacturing facility, so you won’t need to look around.
The timeframe for each order varies depending on the parts structure and specific requirements. We can get your part done within 24 hours. We can provide you with more information if you contact us directly at sales@okdor.com.
The standard surface texture or roughness that we provide is 3.2 μm, AKA as machined. The finishing surface roughness can be applied down to 0.4 μm.
Surface finishing can be performed on metal CNC parts by couple doszen, such as anodizing aluminum parts, blackening steel alloy parts, and powder coating stainless steel parts.
For high-volume production of a few hundred to 1000 parts, CNC machining is the best solution. The most cost-competitive option for producing metal prototypes is CNC machining. CNC machining is also recommended when your parts require extremely tight tolerances.
