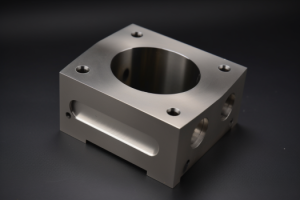
Laser cutting works great for aluminum prototypes, but engineers often hit cost walls when scaling tight-tolerance enclosures to production volumes. With decades of experience helping aerospace and medical teams transition manufacturing processes, small design decisions early can prevent expensive process changes later.
Laser cutting becomes cost-prohibitive above 50-100 pieces due to material waste and setup costs. Alternative cutting methods or CNC machining offer better economics for production volumes, especially for parts thicker than 20mm or requiring tolerances tighter than ±0.037mm.
Learn the specific volume thresholds, design red flags, and cost factors that signal when to transition away from laser cutting for better production economics.
Table of Contents
What Design Features Make Laser Cutting Unsuitable?
Parts thicker than 20mm or requiring complex three-dimensional features cannot be effectively laser cut. Most laser systems handle sheet metal up to 20mm thickness, but beyond this limit, cut quality degrades and alternative processes become necessary.
We regularly encounter aluminum enclosure projects where engineers specify 25mm structural plates, only to discover that laser cutting becomes impractical due to excessive heat buildup and poor edge quality. Our CMM measurements show that 15mm aluminum sections achieve clean cuts with Ra 1.6 μm surface finish, while attempting 25mm thickness results in significant heat-affected zones and requires extensive post-processing. The material thickness limitation becomes even more critical with stainless steel, where thermal expansion during cutting creates dimensional instability that cannot be controlled through standard laser parameters.
Beyond thickness constraints, geometric complexity presents fundamental limitations. Medical device housings requiring internal channels for wire routing or stepped surfaces for component mounting cannot be laser cut effectively since the process is restricted to two-dimensional through-cuts. Audio equipment faceplates with recessed control areas or multi-level surfaces automatically require CNC machining capabilities. We’ve seen projects delayed when teams attempt complex geometries with laser cutting, then discover that assembly features like internal threads, blind holes, or undercuts are impossible to achieve. ISO 2768-m tolerance standards apply to basic laser cut features, but complex assemblies requiring tight geometric controls or precise mating surfaces exceed typical laser cutting capabilities of ±0.050mm.
Design Takeaway: Evaluate part thickness and geometric complexity during initial design reviews. If specifications include materials over 20mm or three-dimensional features beyond simple through-cuts, select CNC machining early to avoid process limitations and unexpected project delays.
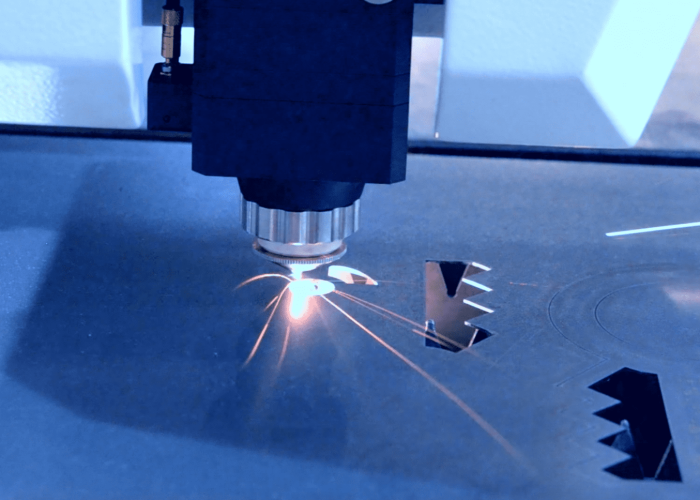
At What Volume Should You Switch From Laser Cutting?
Most projects should transition away from laser cutting above 50-100 pieces due to material waste and setup inefficiencies. The break-even point depends on part complexity, but laser cutting’s per-piece costs remain high while alternative processes scale more efficiently.
We consistently see cost crossovers around 75 pieces for aluminum enclosure components. A recent audio equipment project required 200 faceplate pieces at 3mm thickness – laser cutting quoted $45 per piece due to material waste from kerf width and nesting limitations, while CNC machining dropped to $28 per piece through optimized material utilization. The fundamental issue lies in laser cutting’s fixed setup costs: each sheet requires individual programming and part removal regardless of volume, while CNC machining achieves economies of scale through longer unattended runs.
Medical device components requiring 150-piece runs benefit significantly from CNC machining’s consistent tolerance control across entire batches without thermal variations that affect laser cut quality. Our CMM measurements confirm both processes initially achieve Ra 1.6-3.2 μm finishes, but CNC maintains consistency while laser cutting shows degradation due to lens contamination. ISO 2768-m tolerances remain achievable with both processes, but repeatability favors CNC machining for production quantities.
Design Takeaway: Calculate total project costs including material waste and setup time rather than piece price alone. For volumes above 75-100 pieces, request quotes for both processes to identify true production economics.
How Much More Does Laser Cutting Cost at Higher Volumes?
Laser cutting typically costs 30-50% more than CNC machining for production volumes due to material waste and processing inefficiencies. The cost penalty increases with part complexity, as intricate geometries create significant waste through poor nesting efficiency.
We analyzed a medical housing project requiring 300 units where laser cutting quoted $52 per piece while CNC machining came in at $34 per piece – a 53% cost difference. The primary driver was material utilization: laser cutting achieved only 60% efficiency due to 0.1mm kerf width and spacing requirements, while CNC machining utilized 95% of raw material. Processing speed differences compound these costs, as laser cutting requires multiple sheet setups with individual part handling, while CNC machining processes multiple parts per setup with automated tool changes.
Automation capabilities create the largest cost separation at production volumes. Aerospace components requiring 500+ pieces benefit from CNC’s fully automated cycles that run unattended, while laser cutting demands operator intervention for each sheet change. Material costs escalate with laser cutting due to minimum sheet sizes – small parts often waste 70% of expensive materials. Our surface profilometer measurements show comparable Ra values initially, but laser cutting requires additional deburring operations adding $3-5 per piece.
Design Takeaway: Factor in material waste, secondary operations, and automation efficiency. Above 200 pieces, CNC machining typically delivers 25-40% cost savings while providing superior process consistency.

What Tolerances Can Laser Cutting Actually Achieve?
Laser cutting typically achieves ±0.050mm tolerances, with precision setups reaching ±0.037mm under optimal conditions. These tolerances depend heavily on material thickness, with thinner sheets maintaining better dimensional control than materials approaching the 20mm thickness limit.
We routinely verify laser cut aluminum parts using CMM inspection, achieving ±0.050mm on 6mm thickness with consistent repeatability. However, precision applications requiring ±0.037mm demand advanced laser systems with temperature-controlled environments and optimized cutting parameters. Medical device housings requiring tight assembly fits often push these limits, where we’ve measured variation increasing to ±0.075mm on 15mm stainless steel due to thermal expansion during cutting. The heat-affected zone becomes critical for precision work, as residual stresses can cause dimensional drift during subsequent operations.
Geometric tolerance control presents additional challenges beyond basic dimensional accuracy. Features like hole spacing and edge straightness vary depending on cutting sequence and material properties. Audio equipment faceplates requiring precise control layouts benefit from CNC machining’s ±0.01mm capabilities when assembly tolerances become critical. Our surface profilometer measurements show laser cut edges achieving Ra 1.6-3.2 μm finish quality. ISO 2768-m medium tolerances apply to general features, but functional surfaces requiring tighter control may exceed typical laser cutting capabilities.
Design Takeaway: Reserve ±0.050mm laser cutting tolerances for non-critical dimensions and specify tighter requirements only where functionally necessary. For precision assemblies requiring consistent ±0.025mm or better, consider CNC machining to ensure reliable dimensional control.
What Tolerances Can Laser Cutting Actually Achieve?
Laser cutting typically achieves ±0.050mm tolerances, with precision setups reaching ±0.037mm under optimal conditions. These tolerances depend heavily on material thickness, with thinner sheets maintaining better dimensional control than materials approaching the 20mm thickness limit.
When engineers ask about laser cutting precision, the answer depends entirely on what they’re building. For a 6mm aluminum audio faceplate, our CMM measurements consistently show ±0.050mm accuracy with excellent repeatability. But push that same process to a 15mm medical housing, and suddenly you’re dealing with thermal expansion that can throw dimensions off by ±0.075mm or more. The heat from cutting thick stainless steel creates residual stresses that don’t show up until you try machining secondary features later – then parts start moving as those stresses relieve.
The real challenge comes with geometric features rather than just overall dimensions. Hole patterns for control layouts need tight spacing tolerance, and laser cutting’s sequential heat input can shift later holes relative to earlier ones. That’s where CNC machining’s ±0.01mm capability becomes worth the extra cost for critical assemblies. Surface finish stays consistent at Ra 1.6-3.2 μm regardless of tolerance requirements, but achieving those tighter ±0.037mm tolerances requires controlled environments and optimized parameters that not every shop can maintain. ISO 2768-m covers the general features, but functional surfaces often need specifications beyond what typical laser cutting delivers reliably.
Design Takeaway: Plan for ±0.050mm as your standard laser cutting tolerance, and reserve tighter specifications only where assembly function demands it. If you need consistent ±0.025mm or better across production quantities, the economics usually favor CNC machining despite higher piece prices.

How Do You Choose Between Laser Cutting vs Other Cutting Methods?
Material thickness and required edge quality determine the optimal cutting method – laser cutting excels for sheets under 20mm, while waterjet handles thicker materials and plasma cutting offers speed for structural components. Each process has distinct advantages based on material type and application requirements.
The decision usually comes down to what your part actually needs rather than what sounds most advanced. Last month, an aerospace team wanted laser cutting for 25mm titanium brackets because it seemed like the precision choice. Problem was, laser cutting that thickness creates heat-affected zones that would compromise their subsequent heat treatment. Waterjet solved the problem despite costing more per piece, because it eliminated the thermal stress entirely. Sometimes the “better” process isn’t the obvious one.
For structural steel components where speed matters more than mirror finishes, plasma cutting often makes the most sense. Construction equipment brackets don’t need Ra 1.6 μm edges – they need to be cut fast and cost-effectively. Plasma delivers that with acceptable edge quality for welded assemblies. Meanwhile, stainless steel medical components benefit from laser cutting’s clean edges and minimal distortion, especially when subsequent bending operations are involved. The automation story varies too – laser cutting handles complex geometries beautifully with full CNC control, while plasma excels at repetitive structural shapes where throughput trumps complexity.
Design Takeaway: Match the cutting method to your actual requirements, not your assumptions about what’s “best.” Consider material response, edge quality needs, and downstream operations when selecting the process that delivers the right balance of quality, speed, and cost.
What Are the Risks of Choosing Laser Cutting for Production?
Primary risks include equipment downtime from lens maintenance, limited process scalability, and potential supply chain disruptions from sheet material availability. These operational risks compound at production volumes where consistent delivery schedules become critical for project success.
Production reality hits differently than prototype reality. An audio equipment manufacturer learned this when their 200-piece faceplate run got delayed two days because the laser needed recalibration mid-batch. Lens contamination builds up during extended runs, and suddenly your tight tolerances start drifting without warning. That same job would have run continuously on a CNC machine with predictable tool life and automated operation. The sheet-by-sheet nature of laser cutting means more handling, more setup time, and more opportunities for delays compared to processes that can run multiple parts per setup.
Material supply becomes another headache with complex geometries requiring specific sheet sizes. When your intricate bracket design needs 4×8 sheets of certified titanium, and your supplier has a six-week lead time, your production schedule just became hostage to sheet availability. CNC machining using standard bar stock rarely faces these constraints. Quality control gets trickier too, because gas purity, lens condition, and even sheet flatness affect cut quality in ways that aren’t immediately obvious. By the time you notice the problem, you might have several out-of-spec parts that need rework or scrapping.
Design Takeaway: Build buffer time into production schedules when using laser cutting, and have backup plans for critical deliveries. Consider the full operational picture – equipment reliability, material availability, and process scalability – not just the piece price when planning production volumes.
Conclusion
Laser cutting works best for prototypes and low volumes under 75 pieces, but CNC machining delivers better economics and consistency for production runs. Evaluate thickness, tolerances, and volume early to avoid costly process changes. Contact us to explore manufacturing solutions tailored to your sheet metal cutting and production requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Parts thicker than 20mm or requiring 3D features like internal channels, undercuts, or multi-level surfaces cannot be laser cut effectively. If your design includes these features, plan for CNC machining from the start to avoid redesign costs.
Above 75-100 pieces, laser cutting typically costs 30-50% more than CNC machining due to material waste and setup inefficiencies. Request quotes for both processes when planning production volumes to compare true project costs.
es, but design compatibility varies. Simple 2D geometries transition easily, while complex features may require redesign. Plan for potential part modifications and timeline delays if switching processes mid-project becomes necessary.
Use ±0.050mm for general features and reserve tighter tolerances only for critical assembly surfaces. Specifying unnecessarily tight tolerances increases costs without improving part function in most applications.
Most laser cut parts have acceptable edge quality (Ra 1.6-3.2 μm) for assembly, but deburring may be required for safety or aesthetic reasons. Factor $3-5 per piece for secondary finishing operations in your budget.
Match the process to your material thickness and edge quality needs. Laser cutting works best for sheets under 20mm requiring clean edges, while waterjet handles thicker materials and plasma cutting offers speed for structural components.