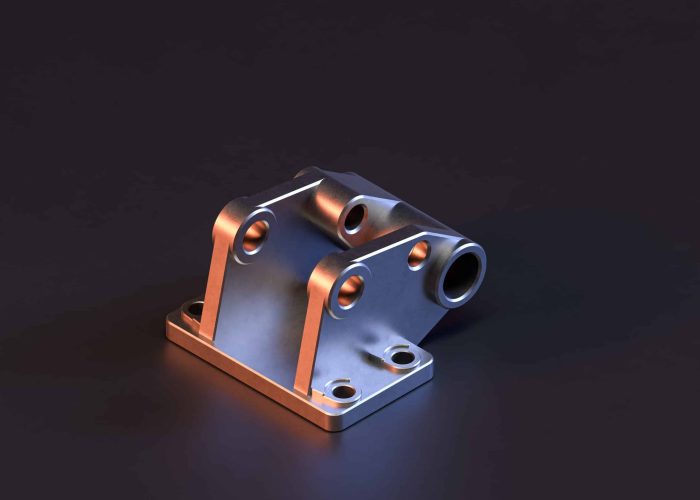
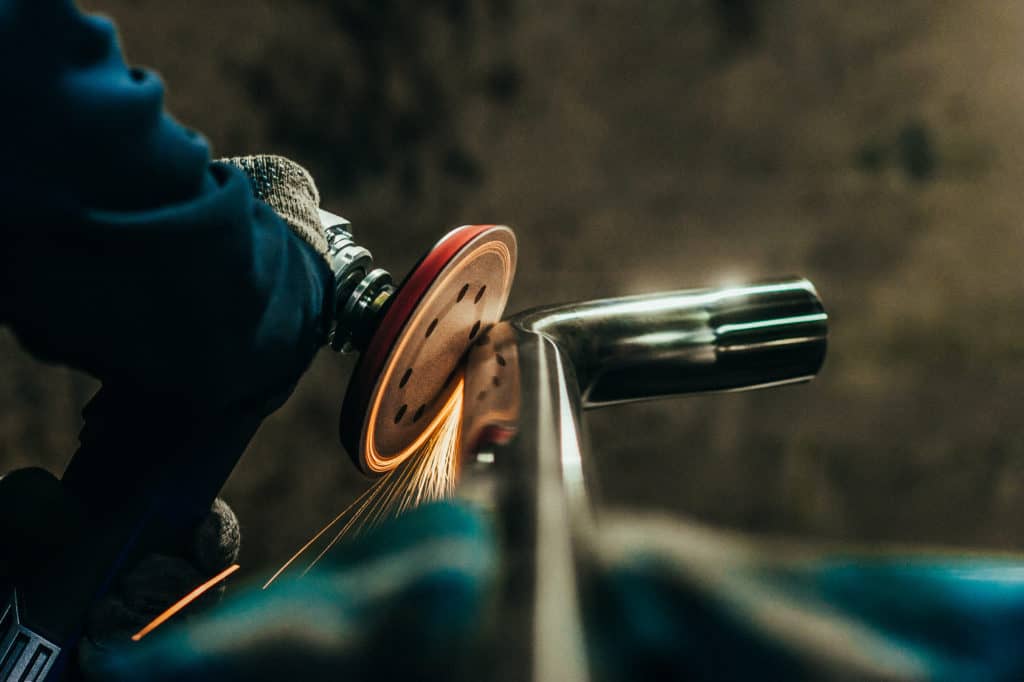
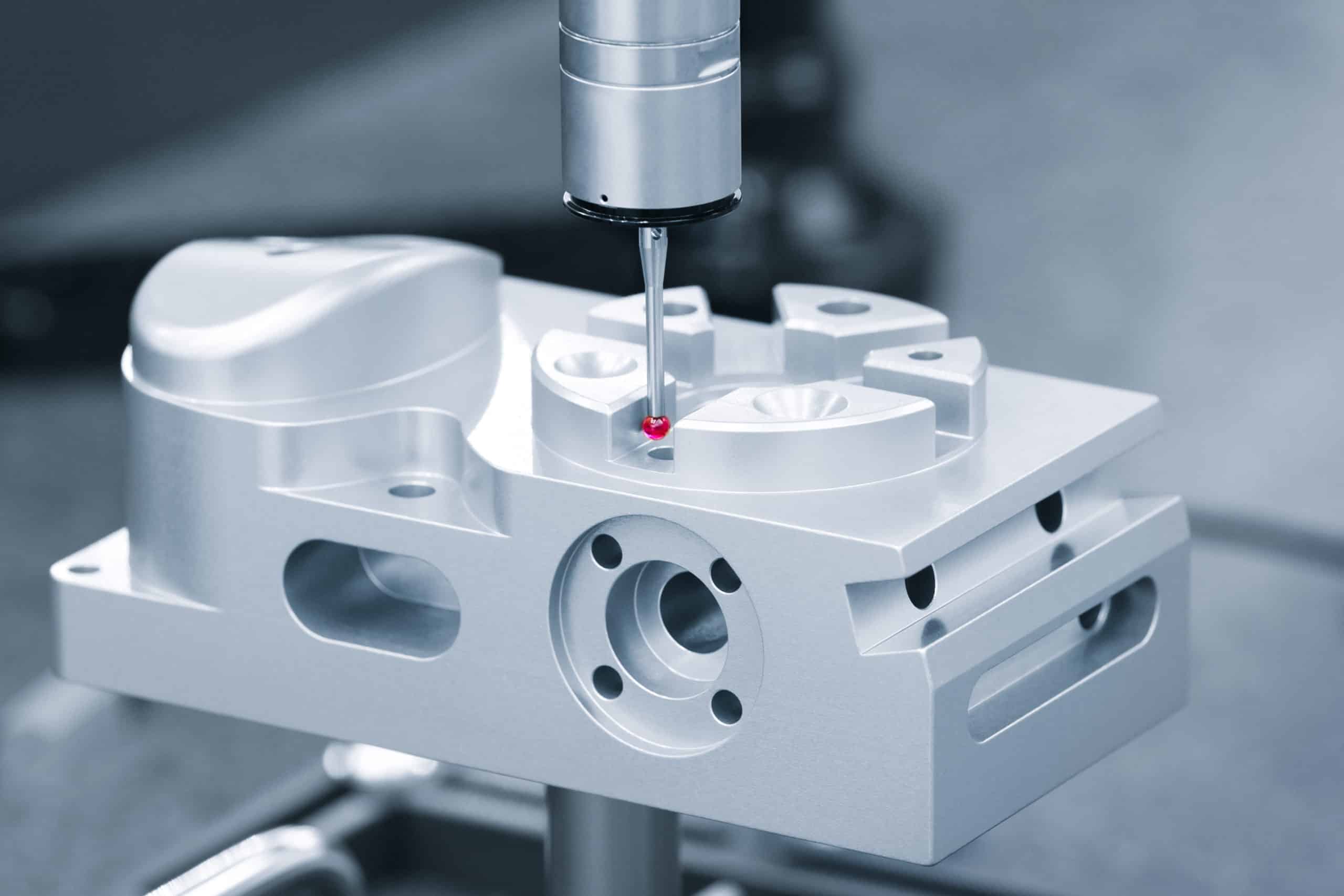
Surface finish decisions impact both cost and performance in precision CNC parts. With experience across aerospace, medical, and audio applications, we help engineers avoid over-specification while ensuring functional requirements are met.
Surface finish selection requires matching functional needs, material compatibility, and operating environment to available treatments. Most applications succeed with standard finishes rather than expensive specialty treatments. Always verify if finishing is functionally required before specifying.
Avoid costly spec errors with a proven decision framework—get tips on drawing callouts, tolerance effects, and when raw surfaces beat treated ones.
Table of Contents
When Can I Skip Surface Finishing to Save Cost and Time?
Raw machined surfaces are sufficient for internal components, structural brackets, and prototypes where function matters more than appearance. Skipping finishing reduces costs by 15-40% and eliminates 3-7 days from delivery schedules.
Standard CNC operations on aluminum and steel consistently produce Ra 1.6-3.2 μm surface finishes, which we verify using Mitutoyo profilometers during final inspection. These machined surfaces handle most assembly tolerances, provide adequate thread engagement for fasteners, and resist galling in steel-on-steel contact applications. Materials like 316 stainless steel and 6061-T6 aluminum offer inherent corrosion resistance that often eliminates protective coating requirements entirely.
We regularly deliver raw machined parts for audio equipment internal brackets, non-patient-contact medical device housings, and aerospace structural components without performance issues. The critical factor is distinguishing where surface treatments solve actual functional problems versus where they’re specified by default. Raw finishes become problematic in outdoor environments, food contact surfaces, or applications requiring specific electrical conductivity values.
Design Takeaway: Challenge every surface finish callout during design reviews. If your part operates in non-corrosive environments, doesn’t require appearance standards, and functions properly with ±0.05 mm standard tolerances, raw machined surfaces deliver the performance you need while keeping costs and lead times minimal.

What Surface Finishes Are Compatible with My Material Choice?
Material compatibility determines which surface treatments are feasible and cost-effective. Aluminum works with anodizing and powder coating, stainless steel excels with electropolishing and passivation, while titanium requires specialized treatments due to its reactive nature.
6061 and 7075 aluminum respond excellently to anodizing, achieving 10-25 μm coating thickness with superior corrosion resistance and color options. We verify anodizing thickness using eddy current gauges to ensure consistent coverage. Powder coating also bonds well to aluminum after proper surface preparation, providing durable finishes for outdoor applications. However, aluminum’s thermal expansion makes electroplating challenging without specialized pretreatment.
304 and 316 stainless steel naturally resist corrosion but benefit from electropolishing to achieve Ra 0.1-0.4 μm mirror finishes essential for medical and food applications. Passivation removes surface contamination while preserving the base material properties. Avoid anodizing on stainless steel—it simply doesn’t work. Titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V require vacuum-based coatings or specialized anodizing processes due to their chemical reactivity, making them more expensive to finish.
Plastic materials like POM and Delrin accept painting and some plating processes but lack the thermal stability for high-temperature treatments like powder coating.
Design Takeaway: Match your material selection to required surface treatments early in design. If you need anodized finishes, specify aluminum alloys. For mirror-polish requirements, choose stainless steel. Don’t force incompatible material-finish combinations that increase cost and complexity.
What Surface Finish Do I Need for My Specific Application?
Functional requirements determine surface finish selection: sealing applications need smooth surfaces (Ra 0.4-1.6 μm), moving parts require wear resistance, and electrical components may need conductive or insulating properties. Match finish specifications to actual performance demands, not general preferences.
Sealing and mating surfaces perform best with Ra 0.8-1.6 μm finishes achieved through machining or light electropolishing. We measure surface roughness using calibrated profilometers to verify O-ring groove compatibility and gasket sealing effectiveness. Rougher surfaces create leak paths, while over-polished surfaces (Ra <0.4 μm) can actually reduce O-ring grip and cause seal failure.
Friction and wear applications benefit from controlled surface textures. Audio equipment sliding mechanisms need consistent 15-25 μm anodizing thickness for smooth operation and scratch resistance. Threaded fasteners require specific roughness ranges—too smooth creates galling, too rough damages threads during assembly.
Electrical conductivity requirements often eliminate coating options entirely. Anodized aluminum blocks electrical contact, while raw aluminum oxidizes and increases resistance over time. Conductive finishes like nickel plating maintain <10 milliohm contact resistance for reliable electrical connections.
Design Takeaway: Define your functional requirements before selecting finishes. Specify Ra values for sealing surfaces, hardness requirements for wear resistance, and conductivity specs for electrical contact. Avoid aesthetic-driven finish selection that compromises function or adds unnecessary cost to non-critical surfaces.
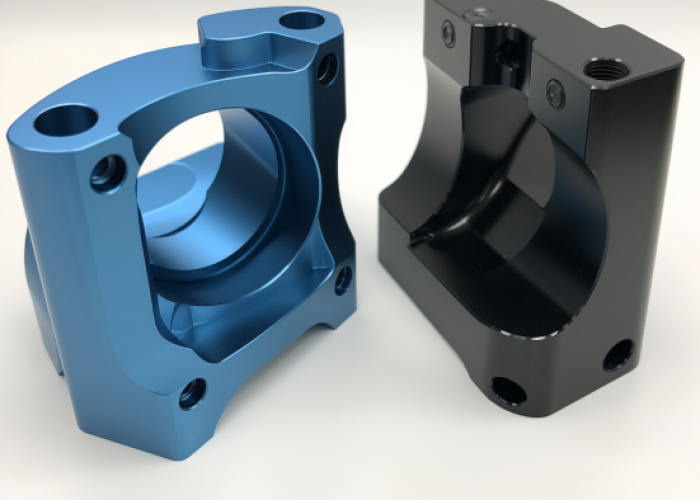
How Does Surface Finish Affect My Assembly and Fit Requirements?
Surface finishing adds thickness that directly impacts tolerances and assembly fits. Anodizing adds 10-25 μm per side, powder coating adds 50-100 μm, while electropolishing removes 5-10 μm of base material. Account for these dimensional changes during design to prevent assembly issues.
Threading applications present the biggest challenges with post-finishing assembly. We regularly see M6x1.0 threads that become tight or unusable after 20 μm anodizing, requiring pre-compensation or post-finishing thread chasing. Powder coating typically requires masking threaded areas entirely, or specifying threads 0.1-0.2 mm oversized to accommodate coating thickness. Internal threads suffer more than external threads due to coating buildup in confined spaces.
Precision fits and bearing surfaces need careful consideration of finish thickness. A ±0.02 mm shaft tolerance becomes problematic when 25 μm anodizing effectively tightens the fit by 0.05 mm total. We measure finished dimensions using calibrated micrometers to verify critical fits still meet specifications. Electropolishing offers an advantage here—it actually opens up tight tolerances by removing material rather than adding thickness.
Mating surfaces and gasket grooves require consistent finish thickness for proper sealing. Uneven coating distribution can create leak paths or prevent proper gasket compression.
Design Takeaway: Add finish thickness to your tolerance stack-up calculations early in design. Specify which surfaces need masking, oversize threaded features by coating thickness, and consider electropolishing for applications where removing material improves rather than compromises the fit.

What's the Real Cost Impact of Different Surface Finishing Options?
Volume determines surface finishing economics more than treatment type. Below 10 pieces, setup costs dominate—anodizing can cost $30-50 per part. Above 25 pieces, per-part costs drop significantly, making specialty finishes viable for production runs.
Setup-driven economics create distinct volume breakpoints that we track across customer projects. Anodizing setup costs of $200-400 spread across 5 prototypes result in $40-80 per part overhead, while 50-piece orders reduce this to $4-8 per part. Powder coating follows similar patterns with lower setup fees but requires specialized masking for threaded or precision surfaces.
Part geometry drives hidden costs through masking and fixturing requirements. We measure finishing time increases of 200-300% for parts requiring thread protection, precise masking lines, or complex fixturing. Simple box-shaped parts minimize these overhead costs, while intricate geometries with internal features can triple finishing expenses beyond base treatment costs.
Production volume strategy should influence finish selection from the design phase. Single prototypes often justify raw finishes or simple bead blasting, while production runs of 25+ pieces make anodizing economically attractive. We help customers identify the volume threshold where premium finishes become cost-competitive with simpler alternatives.
Design Takeaway: Calculate finishing costs at your expected production volumes, not just single-piece pricing. Design parts with finishing economics in mind—minimize masking requirements and choose finishes that scale well with your anticipated order quantities.

How Do I Specify Surface Finish Requirements on My Drawings?
Use Ra values for functional surfaces and general notes for non-critical areas. Specify Ra 0.8 μm for sealing surfaces, Ra 1.6 μm for standard finishes, and Ra 3.2 μm maximum for rough applications. Include finish type, thickness requirements, and masking callouts to prevent manufacturing confusion.
Ra surface roughness callouts provide measurable standards that we verify using calibrated profilometers during inspection. Ra 0.8 μm works for O-ring grooves and gasket surfaces, Ra 1.6 μm handles most general applications, while Ra 3.2 μm suffices for non-critical areas. Avoid specifying unnecessarily tight surface finishes—each step tighter typically doubles machining time and increases cost.
Finish type specifications should include treatment details beyond just “anodize” or “powder coat.” Call out “Clear anodize, Type II, 15-20 μm thickness” or “Powder coat, RAL 7035, 60-80 μm” to eliminate guesswork during quoting and production. Include post-finishing dimensional requirements if critical fits depend on final part dimensions.
Masking and selective finishing require clear drawing annotations. Use leader lines to specify “No finish” areas, thread callouts, and bearing surfaces that need protection. Drawing notes like “Mask all threaded holes” or “Finish all surfaces except as noted” prevent costly mistakes during production setup.
Design Takeaway: Specify surface finishes functionally rather than cosmetically. Use standard Ra values, include finish thickness when tolerances are critical, and clearly mark areas requiring masking. Well-specified drawings reduce quoting time and eliminate expensive revisions during production.
Conclusion
Surface finish selection drives both performance and cost in CNC projects. Focus on functional requirements over aesthetics, account for dimensional changes in tolerances, and specify finishes clearly on drawings. When raw machined surfaces meet your needs, skip finishing to save time and money. Contact us to explore manufacturing solutions tailored to your surface finishing requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Powder coating adds 50-100 μm thickness per surface. Account for this in tolerance calculations—a ±0.05 mm shaft becomes ±0.15 mm after coating both sides. Consider electropolishing for applications where removing material improves fit.
Add 0.05-0.1 mm to thread pitch diameter for 15-20 μm anodizing thickness. M6x1.0 threads typically need 0.075 mm compensation to maintain proper fit after coating. Always specify thread chasing if post-finish assembly is critical.
Anodizing becomes economical around 10-15 pieces due to setup costs. Below this quantity, expect $30-50 per part overhead. Above 25 pieces, per-part costs drop significantly, making specialty finishes viable for production.
Ra 0.8-1.6 μm provides optimal O-ring performance. Smoother surfaces (Ra <0.4 μm) can reduce grip and cause seal failure, while rougher surfaces create leak paths. We verify all sealing surface finishes using calibrated profilometers.
Specify critical surface finishes during design phase to avoid costly redesigns. Reserve ±0.01 mm tolerances and Ra <1.6 μm for functional surfaces only. Let manufacturing recommend finishes for non-critical areas to optimize cost.
Electropolishing removes 5-10 μm while achieving Ra 0.1-0.4 μm finishes, ideal for improving tight fits. Mechanical polishing adds time but works on any material. Choose electropolishing for stainless steel precision parts requiring smooth surfaces.