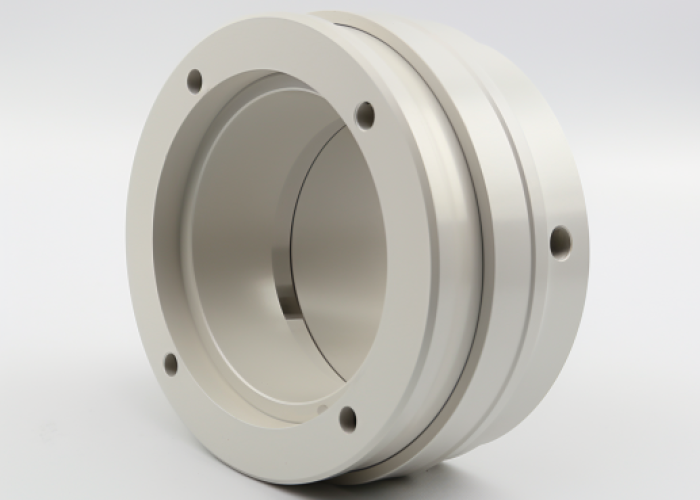
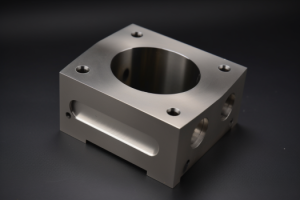
Selecting the right finish for CNC machined parts affects corrosion resistance, assembly performance, and project costs. With over 15 years of precision machining experience across aerospace, medical, and electronics industries, we’ve helped product developers navigate finish decisions that balance protection with budget constraints.
Tin plating is necessary when you need excellent solderability (tin-lead compatibility), FDA food-contact compliance, or mild corrosion protection (96+ hours salt spray resistance). Most CNC parts don’t require tin plating—zinc plating offers better corrosion resistance at lower cost, while anodizing provides superior durability for aluminum components.
Learn when tin plating solves design challenges vs other finishes, plus cost and timeline considerations from real CNC production experience and data.
Table of Contents
What Problems Does Tin Plating Solve?
Tin plating prevents solder joint failures, ensures FDA compliance for direct food contact, and provides indoor corrosion protection. Choose tin plating only if your part will be soldered, directly touches food/beverages, or needs basic corrosion resistance on steel or brass components.
Quick Decision Check: Your part needs tin plating if it meets any of these criteria:
- Circuit board pins, connectors, or terminals that require soldering
- Valve components, nozzles, or surfaces directly contacting food/beverages
- Steel brackets or brass fittings in mildly corrosive indoor environments
Important: Kitchen appliance housings or internal components that don’t directly contact food typically don’t require tin plating.
From our machining experience, tin plating solves specific problems: Circuit board mounting brackets with tin-plated pins provide reliable solder joints where other finishes can create bonding issues. Beverage dispenser valve bodies require it for FDA 21 CFR 175.300 compliance. Steel control panel components use it for rust prevention in humid environments, with typical thickness ranges from 0.0002″ to 0.001″ adding minimal dimensional change.
Tin plating works best on steel and brass substrates but isn’t recommended for aluminum (anodizing performs better). Lead times and costs vary by part complexity and shop capacity. For outdoor applications, zinc plating provides superior weather resistance. High-wear components need harder finishes like Type II anodizing.
Design Takeaway: Specify tin plating only for parts requiring soldering, direct food contact, or steel/brass corrosion protection. Internal appliance components without food contact don’t need it—save cost by choosing simpler finishes.
What Materials Can Be Tin Plated?
Steel, brass, and copper can be reliably tin plated with excellent adhesion and corrosion protection. Aluminum alloys including 6061 and 7075 are not recommended for tin plating due to poor adhesion and potential galvanic corrosion issues.
From our machining experience, choose steel substrates when tin plating is essential for soldering or food contact applications. Carbon steel provides excellent plating adhesion and remains the most cost-effective option for most applications. Keep aluminum and use anodizing instead if your primary concerns are corrosion protection and appearance—this avoids material switching costs and complexity.
Most clients considering material changes discover that anodizing on aluminum meets their actual requirements without the expense of substrate switching. However, when soldering reliability or FDA food contact compliance is mandatory, brass substrates excel for premium food-contact applications due to superior corrosion resistance and reliable plating characteristics.
Stainless steel works well for medical device applications requiring both tin plating and high corrosion resistance, though it requires proper surface preparation for optimal adhesion. We cannot tin plate over existing anodized surfaces—the anodize layer prevents proper plating adhesion.
Design Takeaway: Verify tin plating necessity before changing materials. If required, carbon steel offers reliable performance, while brass provides premium corrosion resistance for demanding food-contact applications.

Does Part Geometry Affect Tin Plating?
Deep blind holes, internal threads, and complex recessed features can receive uneven tin plating coverage. Simple external geometries with through holes and radiused corners plate most consistently and maintain dimensional accuracy.
From our production experience, expect plating challenges with blind holes deeper than 3 times their diameter—solution circulation becomes restricted, leading to thin coverage at the bottom. Internal threads typically work fine for M3 and larger sizes but may show slight thickness buildup affecting engagement with mating hardware.
Through holes and external surfaces receive the most consistent plating because solution flows freely during processing. Sharp internal corners naturally receive less coating thickness compared to external radiused surfaces due to current density distribution during electroplating.
For parts with critical dimensional requirements, account for plating thickness on all exposed surfaces—typically ranging from minimal buildup to noticeable thickness depending on the specific plating process. Complex connector housings with deep internal cavities may require design modifications to ensure adequate plating coverage where corrosion protection is critical.
Design Takeaway: Prioritize external features and through holes for consistent plating results. If internal features are essential, keep blind holes shallow and internal threads M3 or larger to minimize plating-related fit issues.
How Does Tin Plating Compare to Zinc Plating?
Tin plating provides superior solderability and food-contact safety, while zinc plating offers better corrosion resistance and lower cost for general applications. Choose tin plating for electronics assembly or food contact; choose zinc plating for structural components and outdoor applications.
Application Decision Matrix:
- Electronics with solder connections? → Tin plating required (zinc oxide prevents bonding)
- Direct food/beverage contact surfaces? → Tin plating required (FDA 21 CFR 175.300)
- Outdoor structural components? → Zinc plating recommended (superior ASTM B117 performance)
- Mixed-function assemblies? → Design separate components (tin for electrical, zinc for structural)
From our CNC machining and finishing experience, zinc plating typically provides 240+ hours salt spray resistance compared to tin’s 96+ hours per ASTM B117 testing, making zinc significantly better for outdoor applications. However, zinc naturally forms oxide layers that prevent reliable solder joints—we’ve documented assembly failures when clients tried to solder zinc-plated components.
For control panels with both mounting brackets and electrical connections, design them as separate components—zinc-plate the structural housing for durability and tin-plate only the electrical contact areas. This approach optimizes both performance and cost while maintaining assembly simplicity.
Switching from zinc to tin plating typically requires no assembly process changes, but may extend lead times due to specialized shop requirements. Both finishes maintain similar dimensional stability on CNC machined parts.
Design Takeaway: Use zinc plating as your default for 2-3x better corrosion performance. Reserve tin plating exclusively for soldering or food contact—design separate components when both functions are needed.
How Much Does Tin Plating Cost?
Tin plating typically costs significantly more than zinc plating and requires longer lead times due to specialized processing and limited shop availability. Plan for potential project delays and budget increases when specifying tin plating.
Budget Planning Reality Check:
- Expect substantial cost increases over zinc plating → Tin material costs and specialized processing drive premiums
- Small quantities hit hardest → Setup costs spread across fewer parts
- Lead times extend 1-2 weeks minimum → Fewer shops offer tin plating services
- Geographic limitations → May require shipping to distant specialized facilities
From our CNC machining experience, most local plating shops handle zinc plating but require outsourcing for tin plating, extending timelines and adding transportation costs. This becomes critical for project planning—tin plating decisions made late in development can delay product launches.
To justify tin plating costs to procurement teams, focus on functional necessity: soldering reliability that prevents assembly failures, or FDA compliance that enables market access. Document that these benefits cannot be achieved through less expensive alternatives like zinc plating or anodizing.
Risk mitigation strategies include: requesting tin plating quotes during early design phases, identifying backup zinc plating options for non-critical components, and designing modular assemblies that allow finish changes without major redesign. Most tin plating shops prefer minimum orders, so consider batching multiple projects if possible.
Design Takeaway: Plan tin plating requirements early and secure quotes before finalizing designs. Build backup options into your design that allow switching to zinc plating if timeline or budget constraints emerge during development.
How Long Does Tin Plating Take?
Tin plating typically requires longer lead times than standard finishes due to specialized processing requirements and limited shop availability. Rush orders may be possible but carry significant cost premiums and scheduling constraints.
Timeline Planning Quick Check:
- Standard processing: Longer than common finishes like zinc plating or anodizing
- Rush options: Available at specialized shops with premium pricing
- Surface preparation: Proper deburring and cleaning after CNC operations critical for quality
- Batch coordination: Multiple parts can optimize scheduling efficiency
From our CNC manufacturing and finishing partnership experience, proper surface preparation after machining operations directly affects plating timeline and quality. Parts requiring additional deburring, surface conditioning, or fixture modifications take longer to process. We work with clients during design review to optimize part geometry for efficient plating operations, reducing both timeline and cost.
Manufacturing optimization insight: Simple external geometries from standard milling operations typically process more efficiently than complex internal features requiring special handling. We help clients evaluate design modifications that streamline plating operations without compromising function—often improving both timeline and cost performance.
Tin plating’s specialized nature means fewer shops offer these services compared to common finishes, potentially requiring coordination with distant facilities. We recommend planning tin plating requirements early in the manufacturing schedule and securing shop capacity during project planning phases.
Design Takeaway: Plan tin plating requirements during design review phase and coordinate manufacturing schedules early. Consider geometry modifications that streamline plating operations while maintaining functional requirements.
Does Tin Plating Change Part Dimensions?
Tin plating adds thickness to all exposed surfaces, potentially affecting critical fits and threaded connections. Design planning should account for coating buildup on functional surfaces.
Dimensional Planning Quick Check:
- Add clearance to holes and internal features during CNC programming
- Thread engagement may be affected, particularly with smaller thread sizes
- Fixture considerations for masking critical surfaces when necessary
- Surface preparation from machining affects plating uniformity
From our CNC machining and design consultation experience, dimensional control starts with proper machining strategy and finish planning. We recommend adding appropriate clearance during CNC programming rather than trying to compensate through post-machining modifications. Surface quality from machining operations can affect plating uniformity across the part.
Manufacturing trade-off analysis: Masking critical dimensions preserves tight tolerances but adds cost and complexity. Often it’s more cost-effective to design appropriate clearances during the machining phase. We help clients evaluate when design modifications provide better value than selective masking during finishing operations.
Assembly considerations: Multiple plated components in assemblies may accumulate dimensional changes that affect fit and function. During design review, we analyze which surfaces require plating versus which can remain uncoated to maintain critical assembly relationships and reduce finishing costs.
Design Takeaway: Build dimensional considerations into CNC programming during design phase. Collaborate early to optimize part geometry for both machining efficiency and plating requirements without compromising assembly function.
When Do You Need Tin Plating?
You need tin plating when your application specifically requires excellent solderability, FDA-approved food contact surfaces, or electrical conductivity that cannot be achieved through less expensive alternatives.
Application Decision Matrix:
- Electronics requiring soldering: Essential for reliable electrical connections and assembly success
- Direct food/beverage contact: FDA compliance mandatory for market access
- Electrical conductivity needs: Contact surfaces benefit from tin’s conductive properties
- Design optimization opportunity: Often standard finishes provide better value
From our CNC manufacturing experience across electronics, medical, and food processing industries, we help clients avoid over-specifying finishes that add unnecessary cost without functional benefit. Many applications originally specified for tin plating perform well with standard finishes like anodizing or zinc plating, which provide adequate protection with shorter lead times and lower cost.
Proactive design consultation approach: During manufacturability reviews, we evaluate whether tin plating’s specific benefits justify the premium over alternatives. Equipment housings without direct food contact typically don’t require tin plating—standard finishes provide adequate performance. However, electrical connections benefit from tin’s properties even when soldering isn’t the primary requirement.
Cost-reduction through design insight: Consider designing separate tin-plated electrical components within assemblies using standard finishes for structural elements. This optimization strategy provides necessary functionality while minimizing finishing costs and lead times for the overall project.
Design Takeaway: Specify tin plating only for confirmed functional requirements that cannot be met through standard finishes. Partner with us during design review to optimize finish selection for both performance and manufacturability.
Conclusion
Tin plating is necessary only for specific soldering, food-contact, or electrical conductivity requirements—most applications perform better with zinc plating or anodizing at lower cost. Evaluate functional necessity before specifying premium finishes. Contact us to explore manufacturing solutions tailored to your tin plating and CNC machining requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Minimum orders vary significantly by shop specialization, but many tin plating facilities prefer 25-50 piece minimums to justify setup costs. Some shops accept smaller quantities at premium pricing. Contact specialized plating shops early to understand their minimum requirements and pricing structure.
Yes, but requires immediate action and premium pricing. Rush tin plating typically needs minimum 3-day processing time if shop capacity is available. Contact specialized facilities immediately to secure rush slots, as options are limited compared to standard finishes.
Most plating shops can provide sample finishing on test coupons or a few prototype parts. Request samples of both tin and zinc plating on your actual part geometry to evaluate appearance, performance, and assembly compatibility before committing to production quantities.
Tin plating setup costs typically spread more favorably across 100+ parts, though this varies by shop and part complexity. For prototype quantities under 50 parts, the per-part premium is highest. We recommend batching multiple projects or phasing production to reach more economical quantities when possible.
Search for electronics plating services, food-grade finishing shops, or medical device plating specialists in your region. Industry associations and electronics manufacturing directories often list qualified tin plating providers. Plan for potential shipping costs and extended lead times for distant suppliers.
Clearance requirements depend on plating specification and application needs. Consult with your plating provider about expected thickness buildup and add appropriate clearances during CNC programming. Testing with actual mating hardware is recommended for critical applications.