Table of Contents
Sheet Metal Prototyping basics
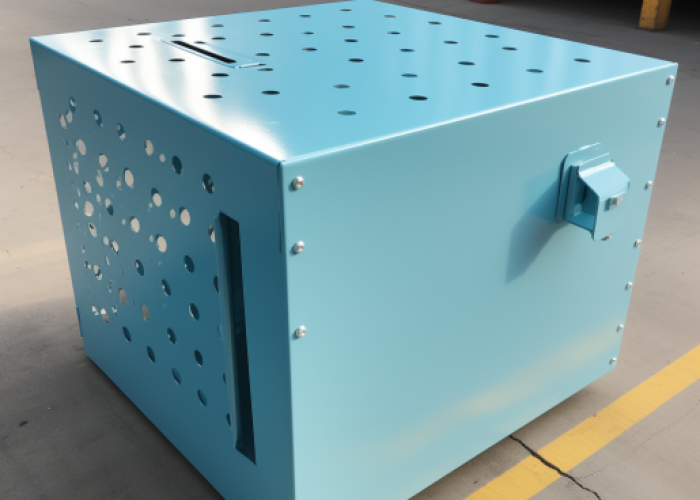
Sheet metal prototyping significantly influences the sheet metal fabrication process. It provides an opportunity to experiment with various compatible materials and assess their performance under different conditions. This process is vital in determining the final product’s most suitable materials and techniques.

The Role of Sheet Metal in Prototyping
Sheet metal, known for its versatility, durability, and corrosion resistance, is popular in fabricating various products. Its ability to form complex shapes makes it an ideal candidate for prototyping.
Utilizing sheet metal in prototyping allows manufacturers to test the functionality and durability of their designs, ensuring they are fit for purpose before initiating high-volume production runs.
The Importance of the Fabrication Process in Prototyping
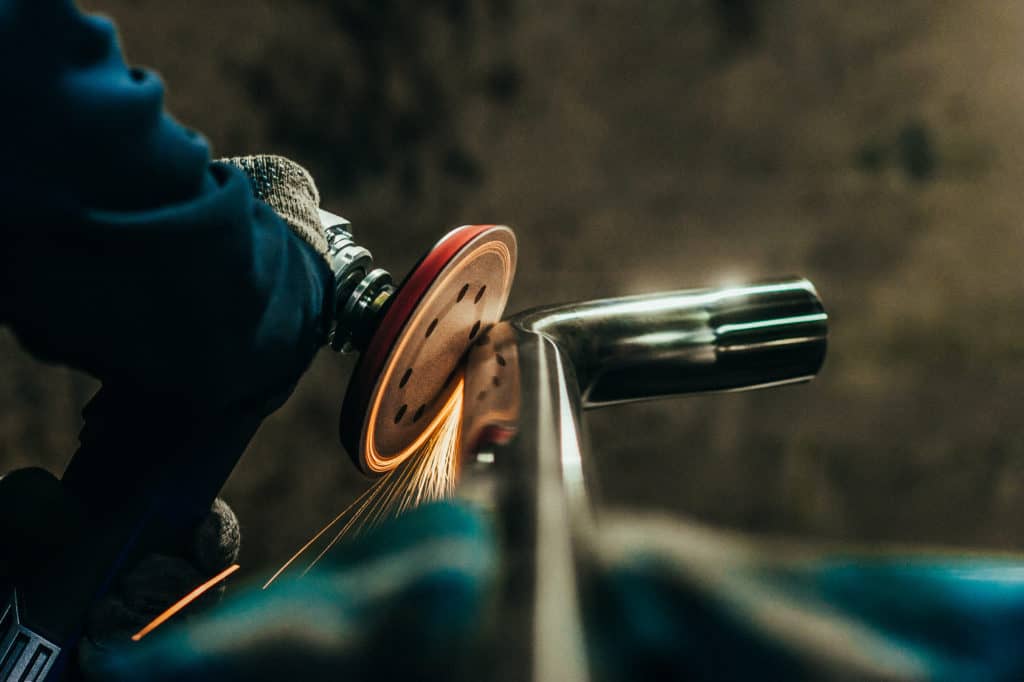
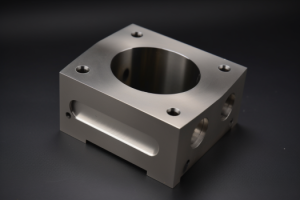
The sheet metal fabrication process encompasses several steps, including laser cutting, bending, and assembling the metal parts. These processes are crucial in creating sheet metal prototypes, allowing manufacturers to test and refine their designs. Prototypes that resemble the final product often use custom sheet metal fabrication.

The Impact of Prototyping on the Final Product
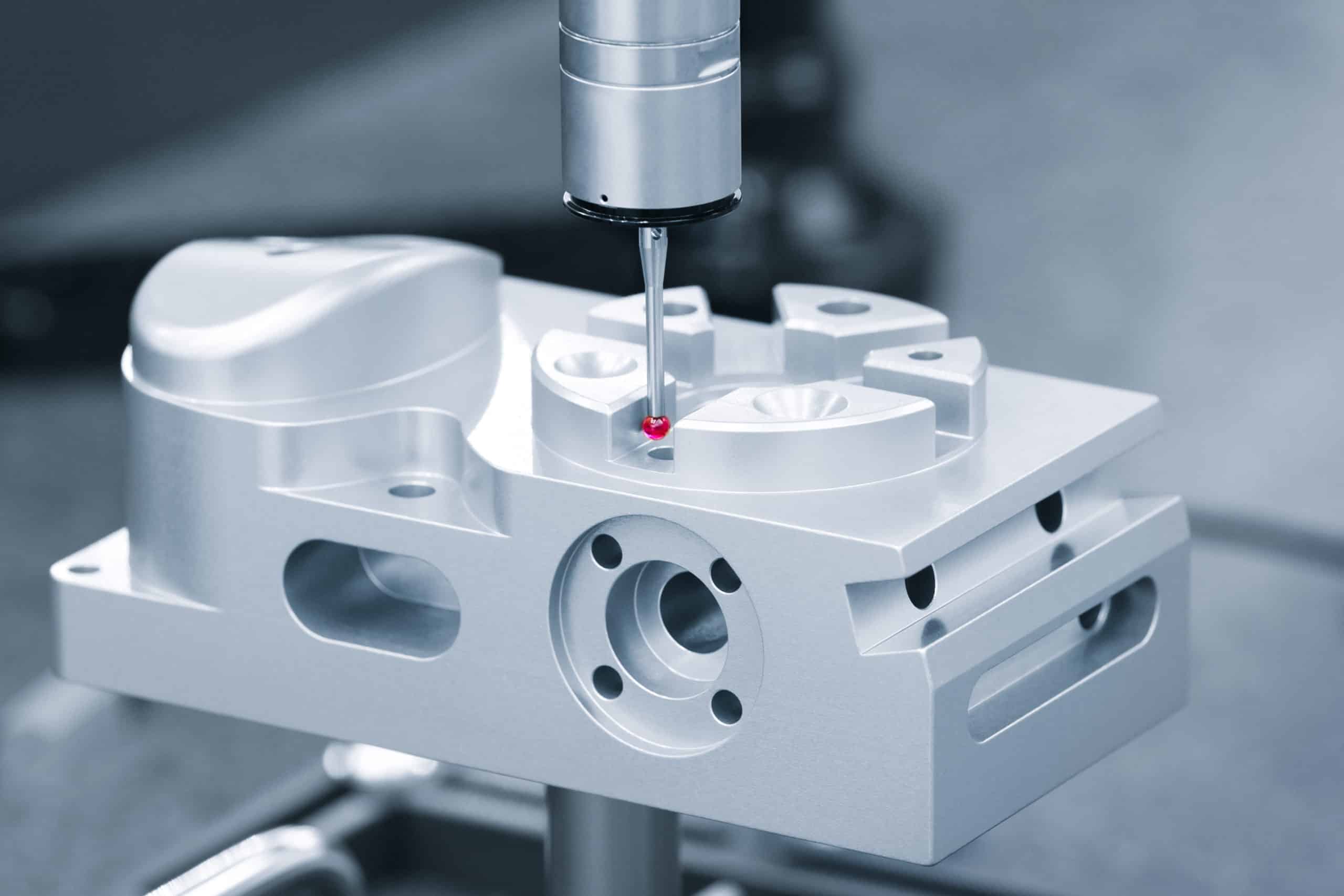
Prototyping plays a significant role in determining the quality of the final product. Manufacturers can ensure that their sheet metal parts meet the desired aesthetic and functional requirements through prototypes.
This process also allows for testing different finishes, such as powder and chromate conversion coating, to determine their impact on the product’s appearance and corrosion resistance.
How Does Sheet Metal Prototyping Benefit, Manufacturers?
Sheet metal prototyping offers several benefits to manufacturers. It allows for testing different sheet metal materials and fabrication processes, producing high-quality sheet metal parts.
The Advantages
- Different sheet metal materials, such as stainless steel and mild steel, offer varying properties that can impact the final product’s performance. Through prototyping, manufacturers can test these materials and select the one that best meets their needs. This process also allows the testing of different sheet metal finishes to enhance the product’s durability and corrosion resistance.
- Custom sheet metal fabrication allows manufacturers to create prototypes that closely resemble the final product. This process enables them to test their designs under real-world conditions and make necessary adjustments. Custom sheet metal fabrication services also allow for the creation of prototypes that traditional sheet metal shops cannot produce due to their complex shapes and designs.
- Through prototyping, manufacturers can ensure the production of high-quality sheet metal parts. This process allows for detecting and correcting errors before the final production, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. Prototyping also enables manufacturers to test their designs under various conditions, ensuring their durability and functionality.
Detailed Process of Sheet Metal Prototyping
Sheet metal prototyping is a multi-step process involving various techniques and tools. Here’s a detailed look at how sheet metal parts are prototyped:
Designing the Prototype
The first step in the sheet metal prototyping process is designing the prototype. This involves creating a detailed 3D model of the final product using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design includes all the final product specifications, such as dimensions, shapes, and features.
The design also considers the properties of the sheet metal materials, such as stainless steel or mild steel, and their electrical conductivity properties.
Material Selection
The next step is selecting the appropriate sheet metal material for the prototype. The choice of material depends on various factors, including the desired properties of the final product, such as corrosion resistance, durability, and strength.
Commonly used materials include stainless steels with good conductivity properties and very little thickness. The material selection process also considers the compatibility of materials with the manufacturing processes.

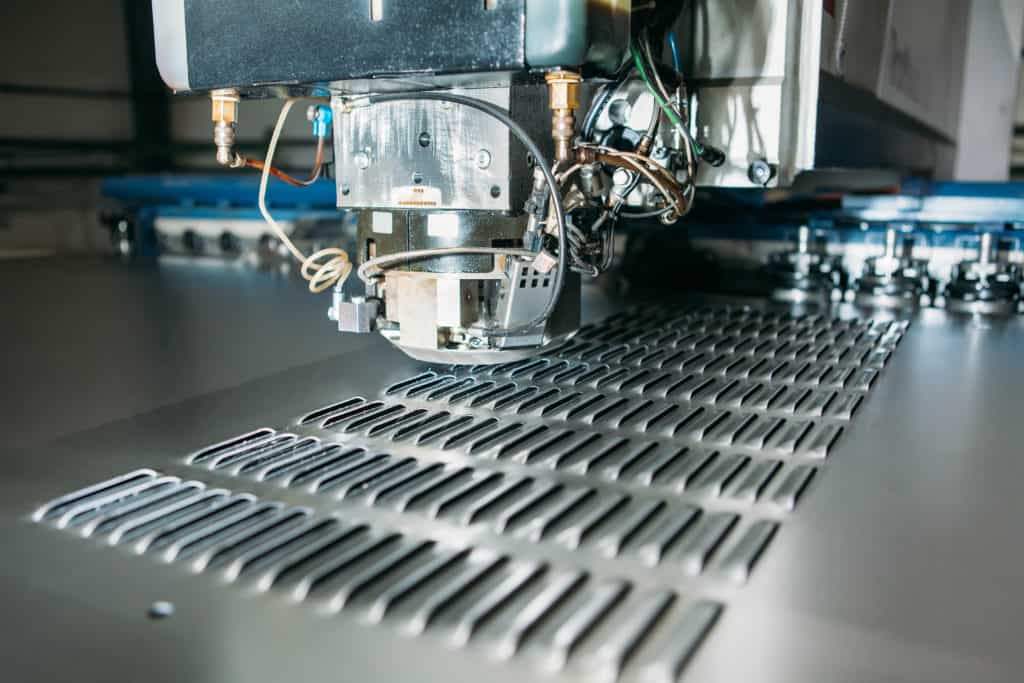
Cutting and Forming
Having finalized the design and selected the material, the next step is cutting and forming the sheet metal. The process usually involves various techniques, such as laser cutting, plasma cutting, waterjet cutting, or CNC machining. These methods use a laser beam, a high-velocity stream of water, or a computer-controlled machine to cut the sheet metal into different shapes per the design.
In addition to cutting, the sheet metal may also need to be formed into different shapes. Sheet metal is bent in specific points according to the design using a press brake. The process can handle both flat sheets and those with complex shapes.
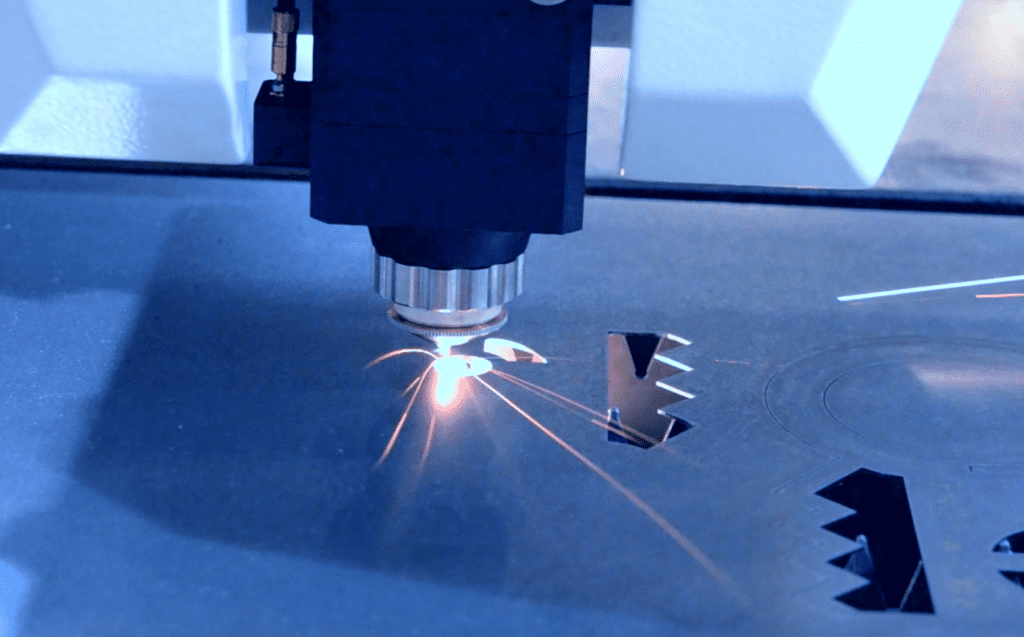
Assembly
Finishing
The final step in the sheet metal prototyping process is finishing. The process involves applying a finish to improve the appearance and corrosion resistance of the prototype. Standard finishes include powder coating, which involves applying powdered paint to the prototype and heating it to form a hard, wear-resistant layer, and chromate conversion coating, which provides a corrosion-resistant finish.
Through this detailed process, sheet metal prototyping allows manufacturers to create accurate and high-quality prototypes of their final products, ensuring any potential issues are addressed before moving on to full-scale production. This process is crucial to manufacturing services, allowing for prototyping and production volumes.

Get Your Prototypes in 24 Hours with okdor!
Imagine having a tangible representation of your final product in your hands in JUST a day. Sounds impossible? Not with Okdor! We’re all about bringing your designs to life quickly and efficiently.
In the manufacturing world, time is important. We have made our processes faster and use machines to make high-quality sheet metal prototypes in only 24 hours.
But speed doesn’t mean we compromise on quality. Our team of skilled professionals ensures that each prototype is crafted to perfection, giving you a reliable model for your final product.
So, why wait for weeks when you can have your prototypes in a day? Reach out to okdor today by sales@okdor.com and let us help you speed up your manufacturing process without compromising on quality. With okdor, fast and efficient service is just a call away!

Conclusion
In conclusion, sheet metal prototyping is crucial in the fabrication process. It allows manufacturers to test their designs and materials, ensuring the production of high-quality sheet metal parts.
Whether it’s testing the corrosion resistance of different finishes or the functionality of complex shapes, prototyping is essential to any sheet metal fabrication work.
Frequently Asked Questions
Online sheet metal fabrication is a service where you can order custom metal parts online. You can upload your design at our get a quote page, and specific your requirement, our team will get back you with details within hours.
Sheet metal fabrication processes include cutting, bending, and assembling. Cutting is possible with a laser, plasma, or shearing with a punch press. Bending is typically done using a press brake machine, and assembly involves joining the cut and formed parts together.
Sheet metal design is crucial as it dictates the final product’s shape, size, and features. It involves creating a detailed 3D model using CAD software, which guides the fabrication process.
A sheet metal fabrication service provides various services, including cutting, bending, forming, assembly, and finishing of sheet metal parts. They may also offer design services and prototyping.
YES. The thickness of the metal sheet depends on the final product’s requirements. Metal sheets of all thicknesses can be used in sheet metal fabrication.
The manufacturing process for metal sheet parts involves the following:
Designing the part.
Selecting the material.
Cutting and forming the sheet metal.
Assembling the parts.
Applying the finish.
This process may also include prototyping and testing.
A subtractive manufacturing process is one where the raw material is removed from a workpiece to create the desired shape. In sheet metal fabrication, this could involve cutting out parts of the sheet metal using a laser or plasma.
The standard painting method for sheet metal parts is typically powder coating. This involves applying powdered paint to the part and heating it to form a hard, corrosion-resistant layer.
Electronic devices, such as CNC machines and laser cutters, are used in sheet metal fabrication to cut and form sheet metal with high precision. The designs are often created on a computer and then fed into these machines as machine code.
Yes, sheet metal fabrication can be cost-effective for low-volume prototypes. Setup costs are relatively low because sheet metal fabrication is relatively inexpensive and adaptable to different designs.
A punch press is used in sheet metal fabrication to cut holes or shapes out of the sheet metal. It uses a shearing force to punch through the metal, creating the desired shape.
Wear resistance is vital in sheet metal fabrication as it determines the durability of the final product. Finishes such as powder coating can enhance the wear resistance of sheet metal parts.